Kodiak Copper (TSXV:KDK) has reported new results for five drill holes at its 25,000-metre drill program at its 100%-owned MPD copper-gold project in British Columbia. The goal of the company’s initial efforts in 2022 was to establish a mining infrastructure, including route development and stockpiling at Gate. The company also worked on developing a mining operation at the site. Drilling on the Gate Zone and nearby look-alike geophysical are underway, with plans for additional drilling in 2022. Drilling revealed new high-grade copper-gold-silver intersections along a 170-meter gap at the Gate end, infilling an existing void. In addition, drill testing geophysical anomalies northeast of Gate has identified a 400-meter long parallel mineralized pattern in the Prime Zone.

Kodiak’s primary focus are its 100% owned copper porphyry projects located in Canada and the USA. The company’s most promising asset is the MPD copper-gold porphyry project situated in the productive Quesnel Trough in south-central British Columbia, Canada. MPD meets all qualifications of a large, multi-centred porphyry system.
Kodiak made the Gate Zone discovery of mineralization with a wide margin, and MPD holds several other targets that are similar and have the potential to be discovered. Kodiak also possesses the Mohave copper-molybdenum-silver porphyry project in Arizona, USA which is located near Bagdad mine. Both of Kodiak’s porphyry projects have historical drilling, as well as present known mineral discoveries that could possibly lead to large-scale deposits.
Claudia Tornquist, President and CEO of Kodiak commented in a press release: “The Gate Zone has delivered further impressive drill intercepts as we continue to increase the size of mineralized envelope which now extends to a kilometer in north-south direction and a depth of 900 metres. We also commenced testing geophysical targets with coincident copper-in-soil signatures in the wider area around the Gate Zone and are pleased that we were able to delineate a parallel mineralized trend at the Prime Zone. This new mineralized trend crystalizes further size potential and validates our model of a large multi-centric porphyry system at MPD. The Company has now expanded its exploration efforts to other high-priority areas like as Dillard and Man and we look forward to this next promising phase of work which should lead to more new discoveries like Gate and Prime across the 147 square kilometre MPD Project area.
Highlights from the results are as follows:
- New drill holes MPD 22-006, MPD-22-008 and MPD-22-05 at the southern end of Gate encountered significant chalcopyrite +/- bornite mineralized intervals, infilling 170 metres of strike and extending the Gate Zone by an additional 50 metres to 900 metres depth. The Gate Zone remains open to depth. Figure 1 and 2
- MPD-22-006 intersected 117 metres of 0.69% Cu, 0.46 g/t Au and 2.22 g/t Ag (1.03% CuEq) within 735.4 metres of 0.24% Cu, 0.14 g/t Au and 0.71 g/t Ag (0.34% CuEq). Table 1, Figures 2 and 4
- MPD-22-008 intersected 59.9 metres of 0.33% Cu, 0.25 g/t Au and 1.77 g/t Ag (0.52% CuEq) within 585 metres of 0.18% Cu, 0.09 g/t Au and 0.71 g/t Ag (0.25% CuEq). Table 1, Figure 2
- MPD-22-005 extended the Gate Zone mineralization to depth and intersected 190.2 metres of 0.19% Cu, 0.12 g/t Au and 1.07 g/t Ag (0.29% CuEq) within 715.2 metres of 0.13% Cu, 0.07 g/t Au and 0.65 g/t Ag (0.19% CuEq). Table 1 Figure 2
- Drilling continues to demonstrate a strong correlation between coincident copper-in-soil anomalies and underlying bedrock copper mineralization, with new copper mineralization discovered adjacent to the Gate Zone at the Prime target. This confirmation is important as new, compelling copper-in-soil targets with coincident geophysical signatures similar to the Gate Zone will be tested by Kodiak through its ongoing, fully-funded drill program in 2022 and 2023. Targets include Dillard, Man, Blue and the 1516 Zones.
- Holes MPD-22-013 and MPD-22-017 intersected a new mineralized trend northeast of, and adjacent to Gate now called the Prime Zone. When combined with historic work, drilling at Prime has identified porphyry-related alteration and copper-gold-silver mineralization over 200 metres width, with 400 metres of strike and down to 550 metres depth.
- MPD-22-013 intersected 180 metres of 0.15% Cu, 0.10 g/t Au and 0.61 g/t Ag (0.22% CuEq) within 330 metres of 0.11% Cu, 0.09 g/t Au and 0.55 g/t Ag (0.17% CuEq). Table 1, Figure 3
- MPD-22-017 intersected 183 metres of 0.16% Cu, 0.07 g/t Au and 0.76 g/t Ag (0.21% CuEq). A second, deeper interval extended into the Gate Zone at 764 meters depth, with 96 metres of assaying 0.28% Cu, 0.14 g/t Au and 0.81 g/t Ag (0.38% CuEq). Table 1, Figure 3
- The extension of the Gate Zone and delineation of the new Prime Zone confirm that recent 3D Induced Polarization (3D IP) surveys are an effective tool for targeting host geology and discovering prospective porphyritic mineralization on the MPD Project. Further work to extend both the Gate and Prime Zones is warranted.
Holes MPD-22-005, 006 and 008 were drilled at various azimuths and inclinations from two pads at the south end of Gate. These holes infilled a 170 metre gap between previous set-ups, while investigating higher grade mineralization and the correlation with 3D IP responses down dip to the east.

Holes MPD-22-013 and MPD-22-017 were drilled westward from sites 400 metres east of the Gate Zone. These holes were drilled to test 3D IP responses at depth and along strike of trenches and shallow drilling on historic Prime claims. New drilling confirmed the continuation of significant copper-gold mineralisation plunging south and dipping to the east, similar to Gate. This trend is called the “Prime Zone” and when combined with previous work, measures 200 metres wide (east-west), with over 400 metres of strike (north-south) and has been drilled down to 550 metres depth. Hole MPD-22-017 continued drilling westward past the Prime Zone and intersected the Gate Zone at 764 meters depth, ending in mineralization at 860 metres downhole.

The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
HighGold Mining (TSXV:HIGH) has reported new assay results from six additional drill holes testing the Ellis Zone at its Difficult Creek Prospect. Difficult Creek is one of several district-scale prospects being explored by HighGold on the Johnson Tract project in Southcentral Alaska, USA.
Darwin Green, CEO of HighGold, commented in a press release: “The Ellis Zone discovery continues to deliver excellent results with some of the strongest and widest intersections to date coming from the western limit of our drilling. We are very encouraged by the persistence of the Ellis Zone mineralization along strike and plan to keep stepping out in all directions as we continue expanding the known extents of the zone. While still very early days, it appears we are well on our way to defining a second deposit at Johnson Tract to compliment the existing high-grade +1Moz JT Deposit mineral resource that is also open to expansion.”
Diamond drilling in the Ongava Continuation zone continues, with fresh step-out holes being drilled on 25 meter centers. With 21.68 grams per tonne Au, 30 grams per tonne Ag, 0.61 percent Cu, and 4.20% Zn over 11.9 meters, these new intersections have extended the region’s broad, high-grade Ellis Zone mineralization nearly 50%.
The JT Deposit (DC Prospect) is located four kilometers northeast of the deposit and is characterized by a series of large gossan alteration zones that are similar in style to the +1Moz AuEq JT Deposit, which covers a 1.5 km x 3.0 km area in a broad northeasterly direction. Gold mineralization and widespread clay/anhydrite alteration are preferentially developed within dacitic to rhyolitic fragmental rocks that are capped by a shallowly dipping sequence of lesser altered andesite volcanics at higher elevations, hosting an epithermal vein field containing gold and silver.
The widespread amount of mineralization exposed in erosional windows by the topping andesite might allow for a large, partially blind mineralized system to be linked between the different DC Prospect zones along a strike length of 3 kilometers. Drilling began in late 2021, and near-surface bonanza-grade mineralization was discovered at 577.9 g/t Au and 2,023 g/t Ag over 6.40 meters in hole DC21-010.
During the off-season, subsequent geology modeling supported a north-northeast striking, steeply north-dipping trend to the mineralization that became the focus of the first 2022 drill program at what is now referred to as the ‘Ellis Zone.’
So far, a total of 36 drill holes have been completed at the Ellis Zone totalling 4,935 meters. Today’s release includes assay results for 6 new holes, making the total number of released holes 14. Drill hole lengths are usually 75 to 150 meters long and have been drilled in fan patterns of 12.5 to 25-meter grid spacing in order refine the geometry, geological controls and grade distribution better understand this promising new mineralized zone.
Mineralogy, veining and alteration at the main JT Deposit are similar to those located four km southwest. The main deposit has been defined from surface downward to a depth of 300 meters, with a strike length of 600 meters and an average true thickness of 40m.
Drilling has now defined the Ellis Zone mineralization over a strike length of approximately 125 meters and from surface to a depth of 100 meters with an average true thickness of 10 to 15 meters. An apparent shallow plunge to the southwest is now defined by the thickest and the greatest-grade intercepts, which suggest that there may be additional targets in this area. The Ellis Zone remains open along strike and at depth, as well as towards the east and west, and drilling continues in ever-increasing increments as confidence in the geologic model grows.

Drill Highlights of the Ellis Zone, DC Prospect are as follows:
Drillhole DC22-046
- 14.8m @ 10.14 g/t Au, 13.8 g/t Ag, 0.28% Cu, 5.97% Zn (14.3 g/t AuEq) including
- 6.8m @ 21.29 g/t Au, 25.1 g/t Ag, 0.55% Cu, 0.61% Pb, 10.70% Zn (28.7 g/t AuEq) including
- 1.5m @ 62.50 g/t Au, 10.5 g/t Ag, 0.77% Cu, 0.59% Pb, 10.59% Zn (70.0 g/t AuEq)
Drillhole DC22-045
- 35.2m @ 4.2 g/t Au, 6.1 g/t Ag, 0.12% Cu, 1.40% Pb, 3.19% Zn (6.7 g/t AuEq) including
- 1.9m @ 12.95 g/t Au, 37.7 g/t Ag, 13.51% Pb, 31.42% Zn (36.2 g/t AuEq), and
- 13.3m @ 7.81 g/t Au, 6.4 g/t Ag, 0.23% Cu, 1.31% Pb, 2.35% Zn (10.0 g/t AuEq)
Drillhole DC22-044
- 20.3m @ 1.72 g/t Au, 5.6 g/t Ag, 0.14% Cu, 1.46% Zn (2.9 g/t AuEq), in hole DC22-044, including
- 2.0m @ 8.34 g/t Au, 8.9 g/t Ag, 0.41% Cu, 4.00% Zn (11.5 g/t AuEq)
Table 1. Johnson Tract Project – DC Prospect – Ellis Zone – Significant Assay Intersections
|
Drill Hole |
From |
To |
Length |
Au |
Ag |
Cu |
Pb |
Zn |
AuEq |
|
(meters) |
(meters) |
(meters) |
(g/t) |
(g/t) |
% |
% |
% |
(g/t) |
|
|
DC22-029 |
31.3 |
32.6 |
1.3 |
6.10 |
6.5 |
0.01 |
0.02 |
0.04 |
6.2 |
|
DC22-031 |
29.2 |
34.3 |
5.1 |
0.31 |
6.7 |
0.03 |
0.10 |
0.23 |
0.6 |
|
DC22-032 |
28.0 |
30.6 |
2.6 |
0.24 |
3.2 |
0.10 |
0.59 |
1.96 |
1.7 |
|
And |
51.1 |
55.6 |
4.5 |
0.26 |
10.2 |
0.11 |
0.90 |
2.56 |
2.3 |
|
DC22-044 |
46.4 |
66.7 |
20.3 |
1.72 |
5.6 |
0.14 |
0.18 |
1.46 |
2.9 |
|
Incl |
52.8 |
54.8 |
2.0 |
8.34 |
8.9 |
0.41 |
0.44 |
4.00 |
11.4 |
|
DC22-045 |
4.6 |
57.1 |
52.5 |
2.95 |
5.5 |
0.10 |
1.01 |
2.38 |
4.9 |
|
Incl |
9.1 |
44.3 |
35.2 |
4.20 |
6.1 |
0.12 |
1.40 |
3.19 |
6.7 |
|
Incl |
9.1 |
11.0 |
1.9 |
12.95 |
37.7 |
0.08 |
13.51 |
31.42 |
36.2 |
|
Incl |
30.0 |
43.3 |
13.3 |
7.81 |
6.4 |
0.23 |
1.31 |
2.35 |
10.0 |
|
DC22-046 |
56.0 |
70.8 |
14.8 |
10.14 |
13.8 |
0.28 |
0.46 |
5.97 |
14.3 |
|
Incl |
56.0 |
65.7 |
9.7 |
15.34 |
20.0 |
0.42 |
0.60 |
8.58 |
21.3 |
|
Incl |
57.5 |
64.3 |
6.8 |
21.29 |
25.1 |
0.55 |
0.61 |
10.70 |
28.7 |
|
Incl |
57.5 |
59.0 |
1.5 |
62.50 |
10.5 |
0.77 |
0.59 |
10.50 |
70.0 |
True thickness for the reported intersections estimated at 50% to 90% of reported width. Gold Equivalent (“AuEq”) based on assumed metal prices of US$1650/oz for Au, US$20/oz for Ag, US$3.50/lb for Cu, US$1.00/lb for Pb and US$1.50/lb for Zn and payable metal recoveries of 97% for Au, 85% for Ag, 85% Cu, 72% Pb and 92% Zn.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The global food supply is becoming increasingly unbalanced, as conditions like conflict and drought continue to rise. This has led to a situation where a few countries now control the potash market, which is essential for ensuring global food security. Brazil Potash’s Autazes Project aims to change that by doubling output in the coming years and making Brazil self-sufficient in terms of potash production in the near future. Here’s why it could be a key investment for global food security.
The Potash Market Has Strong Fundamentals
The demand for potash is driven by a number of factors, including population growth, urbanization, and the need for higher-yielding crops. This means that the market fundamentals are strong and continue to support higher prices. There is a highly concentrated supply side with price support and further upside potential because of the sanctions placed on Belarus and Russia. Countries like Brazil that have the potential to increase production are in a strong position to take advantage of this situation.
It is also the best option as a fertilizer, with the lowest environmental footprint and constant demand. The barrier is that crop area and yields need to rise.
Investment in Food Security is a Multi-Generational One
Feeding the world’s growing population is an ongoing challenge that requires a long-term commitment. Investing in food security is not something that can be done overnight, but rather it is a multi-generational effort. Brazil Potash’s Autazes Project is one example of how this type of investment can pay off in the long run. By increasing production and making Brazil self-sufficient in terms of potash production, the project has the potential to make a significant impact on global food security for decades to come.
The Company Has a Leading ESG Profile
Brazil Potash is a company with a strong commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. This is evident in their Autazes Project, which aims to double output while also protecting the environment. The company has also taken steps to ensure that the local community will benefit from the project, through initiatives like training programs and infrastructure development. This leading ESG profile is another reason why Brazil Potash’s Autazes Project could be a key investment for global food security.
Brazil is Currently an Import-Dependent Market With Growing Demand
Brazil is currently a net importer of potash, due to a combination of factors like limited production and growing demand. With Brazilian demand expected to continue growing, the project has the potential to make a huge dent in the demand domestically. The country is the world’s largest net exporter of agricultural products and food but requires potash imports to hit those numbers. This could be solved with domestic potash production which would drive down agricultural input costs immensely.
Brazil is also a naturally advantageous market for agriculture with significant amounts of arable land, freshwater, and exports for agricultural goods of approximately $110 billion.
Management Has a Strong Track Record
Brazil Potash has an extremely experienced management team with backgrounds from Vale, Shell, Rio Tinto, BHP Billiton, Hatch, and Nutrien. The team has a strong track record of developing and bringing projects into production. In addition, the company’s board of directors includes advice from representatives from some of the world’s largest agribusiness companies, which provides valuable insights into the industry.
The project has received strong support from the Brazilian government as well, and fertilizers have become a national priority since the release of the National Fertilizer Plan.
Bringing a massive potash project to production like Autazes has the potential to swing the balance of power in the potash market and increase Brazil’s role as a key player in global food security. With strong fundamentals, a committed management team, and a supportive government, Brazil Potash’s Autazes Project could be the one to do so.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

On Monday September 12, 2022, Adriano Espeschit, president of Brazil Potash presented the Autazes Project to representatives of the Canadian government and Canadian companies at an event called “Breakfast Procurement Needs” held at Mercure Lourdes hotel in Belo Horizonte.
“The event was organized by the government of Canada, which brought Canadian companies interested in new projects here in Brazil. Then, several companies presented their projects. And Potássio do Brasil made a point of being present presenting the Potássio Autazes Project”, said the president of Brazil Potash.
At the event, there were representatives from the federal government of Canada, the Mining Suppliers and Trade Association, the Province of Québec, and the Chamber of Commerce Brazil/Canada. In addition, several Canadian companies sent representatives to participate.
The Autazes Project is a sustainability engineering investment for the production of Potassium Chloride – an important fertilizer for Brazilian agribusiness – in the municipality of Autazes. The distance from Manaus is 112 km.
The project will employ a process for extracting Silvinite, a rock made up of halite (salt) and Silvita (potassium chloride), which will not harm the earth’s surface soil or environment. The chambers and pillars technique will be utilized throughout the entire extraction operation.
In order to remove the ore, which is approximately 800 meters deep, the company will need to excavate two shafts. The Silvinite ore will be brought to the surface through these wells, and processed so that the Potassium Chloride (fertilizer) can be separated from the Sodium Chloride (kitchen salt).
After the separation of Potassium Chloride and Sodium Chloride, the fertilizer will be transported via barges from a private port that is to be built by the company on the bank of the Madeira River. The market they are aiming this product toward is Brazilian agribusiness consumers.
“The Sodium Chloride will be stored in an impermeable place to protect the soil and the water table, and then it will return to the subsoil, filling the open chambers, that is, there will be no residues on the surface at the end of the Project’s useful life”, explains the president of Brazil Potash.
The project, which is now in the environmental licensing stage, has a predicted useful life of more than 23 years and will put Amazonas state among Brazil’s top fertilizer producers. When it reaches the average annual production of 2.4 million tons of Potassium Chloride, this input will meet roughly 20% of Brazilian demand. Preliminary studies, on the other hand, indicate that production capacity may be expanded up to 45% of Brazilian demands. The project will be soon implemented, and in turn, guarantee tax revenues for the Municipality, State and Union.
As a result, Brazil Potash will aid in the reduction of dependency on imports from countries such as Canada, Russia, Belarus, Germany, and Israel. It’s worth noting that Brazil is at present the world’s second-largest consumer of potassium but only produces 5% of its consumption need.
Potássio do Brasil Ltda. (controlled by Brazil Potash) is a private Brazilian company that manufactures fertilizers. It has been present in the Amazon region since 2009 and has British, Australian, Canadian and Brazilian investors with more to come as the project expands. The potassium ore will be extracted and treated in Amazonas before being turned into fertilizer.
The Autazes Project is in the environmental licensing phase with the Institute for Environmental Protection of Amazonas (Ipaam) as the competent body to license projects in Amazonas state. The LP is available, and the Installation License is pending.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The global demand for minerals has placed a spotlight on the need for a stronger industrial base, one that includes more domestic production and processing of metals that are critical for a modern society. Energy security is strongly linked to mining, as minerals are essential ingredients in the production of energy technologies. Despite the critical role of minerals in securing economic futures and the protection of our planet, the U.S. continues to delay many high-value mining projects while deepening import dependence on the materials they provide.
Current energy disruptions have made it even more clear that a mineral and metals supply chain that relies heavily on a handful of countries can make the whole chain weak. Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the U.S. and EU have looked for ways to reduce their dependence on Russian natural gas. One promising solution is to develop shale gas resources in the United States, which would help create jobs and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, this process requires large amounts of minerals, such as sand, clay, and limestone – all of which are in short supply.
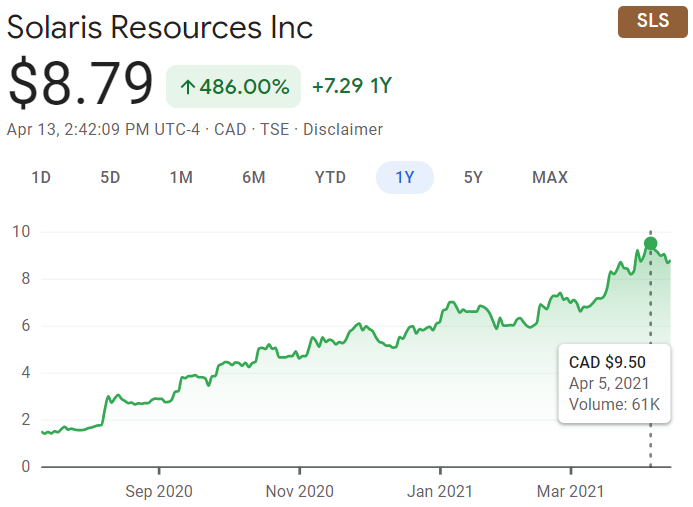
Copper is another tight market being squeezed due to other supply chain issues that were exacerbated during the COVID-19 pandemic. New projects are in short supply, so companies are often eager to acquire new high-grade copper projects when they become available. The Warintza Project in southeastern Ecuador is operated by Solaris Resources (TSX:SLS) a junior mining company that is currently advancing the project towards production.
The Warintza Project has the potential to fill some of the gaps in the current copper market. The project is expected to produce approximately 100 million pounds of copper per year, making it one of the largest copper mines in Ecuador. In addition, the Warintza Project has been called a potential “super pit”, and has released a mineral resource estimate for a significant ‘Indicative Starter Pit’. The company reported in-pit resources of 579 Mt at 0.59% CuEq (Ind) and 887 Mt at 0.47% CuEq (Inf), and 180 Mt at 0.82% CuEq (Ind) and 107 Mt at 0.73% CuEq (Inf) at the time. Most recently, Solaris reported assay results from a series of holes aimed at growing the Northeast Extension of the ‘Indicative Starter Pit’.
Copper is another area the United States and many other countries are looking to lower import dependence. Companies like Tesla, a large consumer of copper for car and battery technology, have been vocal about their desire to source minerals from North America. The Warintza Project could play a role in meeting this demand, as it is located in an area with good infrastructure and a skilled workforce.
The vulnerability of the energy industry has accelerated the calls for renewable energy sources that would reduce or eliminate the dependence on oil and gas from other countries. To bolster domestic supply, it will require projects like the Warintza Project to fill the demand that continues to grow faster than supply. Junior mining companies will play a larger role in a future of energy security than ever before.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

As the world becomes increasingly digitized and reliant on technology, the demand for copper continues to grow. Copper is used in everything from smartphones to power grids, and the mining and production of this valuable metal has a significant environmental impact. However, thanks to recent innovations in mining and production technology, we may be able to meet this growing demand without harming the environment.
Companies engaged in copper exploration are currently leading the charge toward a greener future for the industry. One such company is Rio Tinto, which has been working on developing a new method of extracting copper from ore that doesn’t require smelting. Smelting is a process that releases harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, so eliminating it would be a major step forward in terms of reducing the environmental impact of copper mining.
Another great example is Solaris Resources (TSX:SLS) which has signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Electric Corporation of Ecuador (“CELEC EP”) to supply low-cost, locally sourced hydroelectric power to the Warintza Project (“Warintza” or “the Project”) in southeastern Ecuador.
CELEC EP will source hydroelectric power from the National Transmission System in Ecuador to provide primary power required for the Warintza Project. This initiative is consistent with the “Ecuador Zero Carbon Program” developed by the Ministry of Environment, Water and Ecological Transition and Solaris was the first mining signatory of September 2021.
Solaris wants to make the most of this efficient, renewable, and cheap energy source by investigating how to electrify infrastructure like mobile mining equipment (e.g., drills, trucks), goods transportation (including gravity-assisted solutions), and processing and pumping systems.
Daniel Earle, President & CEO, commented in a press release: “The MOU with CELEC supports our vision to study the potential for electrified operations that maximize the structural benefits of the Warintza Project within an infrastructure-rich mining district with the aim of lowering costs, increasing efficiencies, reducing emissions, and broadly positioning the Project as a leading development opportunity across a range of financial and ESG metrics in the industry.”
Supplying power for the infrastructure and mining activities at Warintza with renewable energy will help to offset the environmental impact of the project, and could set a precedent for other mines in the area.
Other companies have also looked at switching transportation to a net-zero emissions model, in which electric vehicles are powered by renewable energy sources. This would not only reduce emissions from the mining process itself, but also from the transportation of copper ore to processing plants.
Considering copper is one of the key elements powering the transition to renewable energy, it’s encouraging to see the exploration and production industry working hard to reduce its environmental impact. With continued research and development, companies like Solaris Resources are driving the mission toward net-zero forward faster than ever.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
Vizsla Silver (TSXV:VZLA) has announced new results from 13 new drill holes targeting the Cruz Negra Vein in the western portion of the district. The company has reported it has expanded mineralization of West Napolean, and has added new claims at the same time at the 100%-owned Panuco silver-gold project in Mexico.
The results are based on the Cruz Negra Vein, which is 250 meters west of the Napoleon mining area. The northwest and southeast extensions of Cruz Negra, which are currently located on pre-existing Vizsla claims and cover approximately 400 meters of new potentially mineralized vein strike to explore, were added to the claim portfolio.

The Vein of the Cruz Negra, 250 meters west of the Napoleon deposit, is an intensely dipping northwest striking vein-breccia. The quartz veining and disseminated sphalerite and galena in the vein breccia are caused by quartz cement bearing disseminated sphalerite and galena. Drilling to date has tested Cruz Negra at a depth of approximately 400 meters from the Josephine Vein.
Furthermore, hole NP-22-293 studied the possible northwest extension and yielded 535 g/t AgEq over 0.76 mTW, revealing that the mineralization extends for another 500 metres on the newly acquired claims. The drilling also displayed potential vein splays or cymoid loops that could significantly impact silver and gold grades.
At Cruz Negra, mineralized intercepts have estimated true widths ranging from 0.65 to 3.10 metres, with grades ranging from 265 to 3,499 g/t AgEq. Mineralization is open at depth and northwest of the current drilling area, where Vizsla plans to complete detailed mapping and start drilling again in the near future to explore the 500 metre gap between known areas of mineralization.
Vizsla’s organic growth plan was implemented in the acquisition of two claims, with a combined surface area of 14.75 hectares that filled most of the 500 m gap between the open-ended intercepts.
Michael Konnert, President and CEO of Vizsla, commented in a press release: “Our ongoing mapping and sampling efforts in the western area of the district have highlighted several new drill ready targets including Cruz Negra. Initial drill results demonstrate mineralized continuity over approximately 400 metres long with large step outs to the northwest, suggesting the vein continues for at least another 500 metres. Our exploration team has done a phenomenal job this year identifying and expanding new mineralized structures directly outboard of the March 2022 resource areas. As of early September, we have achieved data cut-off for inclusion in the updated resource, slated for mid-December, and anticipate a material increase to contained precious metals.”

Highlights from the results are as follows:
- NP-22-274 returned 541 grams per tonne (g/t) silver equivalent (AgEq) over 2.09 metres true width (mTW) (413 g/t silver, 1.99 g/t gold, 0.16% Pb and 0.27% Zn)
- And 357 g/t AgEq over 0.88 mTW (258 g/t silver, 1.54 g/t gold, 0.01% Pb and 0.17% Zn)
- NP-22-262 returned 1,476 g/t AgEq over 0.65 mTW (168 g/t silver, 16.42 g/t gold, 0.86% Pb and 3.26% Zn)
- NP-22-290 returned 491 g/t AgEq over 2.85 mTW (76 g/t silver, 2.60 g/t gold, 0.57% Pb and 6.19% Zn)
- NP-22-293 returned 535 g/t AgEq over 0.76 mTW (481 g/t silver, 1.20 g/t gold, 0.02% Zn and 0.02% Pb)
- NP-22-298 returned 456 g/t AgEq over 1.60 mTW (297 g/t silver, 1.78 g/t gold, 0.31% Pb and 1.23% Zn)
|
Drillhole |
From |
To |
Downhole |
Estimated |
Ag |
Au |
Pb |
Zn |
AgEq |
Vein |
||
|
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
(g/t) |
(g/t) |
% |
% |
(g/t) |
||||
|
NP-22-257 |
100.50 |
102.00 |
1.50 |
1.00 |
142 |
1.14 |
0.43 |
3.73 |
357 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
Includes |
101.40 |
102.00 |
0.60 |
0.40 |
316 |
2.72 |
0.53 |
6.50 |
734 |
|||
|
NP-22-262 |
191.60 |
193.35 |
1.75 |
0.65 |
289 |
2.38 |
0.77 |
0.70 |
486 |
HW vein |
||
|
Includes |
191.60 |
192.15 |
0.55 |
0.20 |
741 |
5.88 |
0.33 |
1.26 |
1,165 |
|||
|
NP-22-262 |
253.25 |
255.00 |
1.75 |
0.65 |
168 |
16.42 |
0.86 |
3.26 |
1,476 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
Includes |
253.25 |
254.50 |
1.25 |
0.46 |
181 |
19.70 |
1.06 |
3.78 |
1,748 |
|||
|
NP-22-266 |
No significant values |
|||||||||||
|
NP-22-267 |
No significant values |
|||||||||||
|
NP-22-274 |
166.05 |
168.90 |
2.85 |
2.09 |
413 |
1.99 |
0.16 |
0.27 |
541 |
HW vein |
||
|
Includes |
168.55 |
168.90 |
0.35 |
0.26 |
2,490 |
12.85 |
0.61 |
0.87 |
3,287 |
|||
|
NP-22-274 |
193.30 |
194.50 |
1.20 |
0.88 |
258 |
1.54 |
0.01 |
0.17 |
357 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-279 |
172.20 |
174.35 |
2.15 |
1.53 |
72 |
0.56 |
0.07 |
0.34 |
121 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-280 |
205.55 |
207.40 |
1.85 |
1.00 |
187 |
1.40 |
0.15 |
0.39 |
292 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-280 |
224.15 |
226.70 |
2.55 |
1.38 |
91 |
0.73 |
0.22 |
0.64 |
137 |
FW vein |
||
|
NP-22-285 |
272.15 |
274.50 |
2.35 |
0.75 |
40 |
1.21 |
0.01 |
1.81 |
189 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-287* |
274.30 |
274.80 |
0.50 |
0.40 |
402 |
1.82 |
0.10 |
0.21 |
505 |
FW vein |
||
|
NP-22-290 |
356.00 |
360.05 |
4.05 |
2.85 |
76 |
2.60 |
0.57 |
6.19 |
491 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-293* |
12.10 |
13.30 |
1.20 |
0.76 |
481 |
1.20 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
535 |
|||
|
NP-22-294 |
378.85 |
379.85 |
1.00 |
0.70 |
66 |
0.43 |
1.27 |
3.91 |
265 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
NP-22-298 |
380.50 |
383.05 |
2.55 |
1.60 |
297 |
1.78 |
0.31 |
1.23 |
456 |
Cruz Negra |
||
|
Table 1: |
Downhole drill intersections from the holes reported Cruz Negra vein on the Napoleon area. Note: AgEq = Ag ppm x Ag rec. + (((Au ppm x Au rec. x Au price/gram) + (Pb% x Pb rec. x Pb price/t) + (Zn% x Zn rec. x Zn price/t))/Ag price/gram). Metal price assumptions are $20.70/oz silver, $1,655/oz gold, $1,902/t lead and$2,505/t zinc. Metallurgical recoveries applied in the calculation (93% for silver, 90% for gold, 94% for lead and 94 % for zinc), were determined for the Napoleon vein (see press release dated February 17, 2022). NP-22-287* and NP-22-293* were drilled over 500 m NW from Cruz Negra vein intercepts. |
|
Drillhole |
Easting |
Northing |
Elevation |
Azimuth |
Dip |
Depth |
|
NP-22-257 |
403,165 |
2,587,117 |
526 |
237.0 |
-59.0 |
192 |
|
NP-22-262 |
403,165 |
2,587,117 |
526 |
304.0 |
-60.0 |
414 |
|
NP-22-266 |
403,171 |
2,587,335 |
534 |
233.0 |
-53.2 |
411 |
|
NP-22-267 |
403,171 |
2,587,335 |
534 |
229.0 |
-44.7 |
354 |
|
NP-22-274 |
403,112 |
2,587,278 |
575 |
230.0 |
-53.2 |
315 |
|
NP-22-279 |
403,112 |
2,587,279 |
575 |
258.0 |
-52.3 |
342 |
|
NP-22-280 |
403,112 |
2,587,279 |
575 |
259.0 |
-61.3 |
423 |
|
NP-22-285 |
403,112 |
2,587,279 |
575 |
263.0 |
-67.9 |
423 |
|
NP-22-287 |
402,772 |
2,587,806 |
465 |
248.0 |
-45.0 |
340 |
|
NP-22-290 |
403,171 |
2,587,335 |
534 |
250.0 |
-59.2 |
417 |
|
NP-22-293 |
402,772 |
2,587,806 |
465 |
249.0 |
-53.3 |
380 |
|
NP-22-294 |
403,167 |
2,587,335 |
541 |
251.0 |
-65.6 |
480 |
|
NP-22-298 |
403,268 |
2,587,318 |
511 |
250.0 |
-45.5 |
465 |
|
|
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
Enduro Metals (TSXV:ENDR) has completed its 2022 drill program consisting of 10,888 metres of diamond drilling over 25 holes at the Newmont Lake Project.
The 2022 drilling campaign’s purpose was to expand the Burgundy Ridge copper-gold porphyry target’s mineralized footprint, following 2021’s discovery hole (331m of 0.71% CuEq from surface, including 146m of 1.00% CuEq). A total of 20 diamond drill holes were completed at Burgundy Ridge during the season. An additional 5 diamond drill holes were completed at McLymont West along the McLymont Fault Gold Mineralization Zone.
Over the course of several months in 2018, Enduro conducted drone magnetic geophysical surveying and geological mapping, as well as significant channel sampling throughout other Newmont Lake project locations to ensure a steady supply of high-priority targets.
Enduro’s 2022 exploration program was based on the successes of 2021. In that year, they drilled several promising target areas including Burgundy Ridge, 72 Zone, NW Zone, Havana and Chachi. They have received all assay results from those tests and will post them to their website.
Cole Evans, President/CEO of Enduro Metals commented in a press release: “We are thrilled to report that our team has completed the largest drill program undertaken at the Newmont Lake project. Given the scale of the property, the number of exploration targets, and the cost of exploration in the Golden Triangle, a decision was taken to concentrate the 2022 exploration budget on expanding the mineralized footprint of the Burgundy Ridge copper-gold porphyry discovery which I believe has the potential to be a Tier 1 mineral deposit. In addition to drilling at Burgundy Ridge, we put 5 holes into the McLymont West target within the McLymont Fault Gold Zone. I am encouraged by what I have seen in the drill core from both areas and look forward to receiving assays later in 2022″.
Dylan Hunko, COO of Enduro Metals commented in a press release: “We are very pleased with the 2022 exploration season and with the real progress Enduro has made advancing the targets at Burgundy Ridge and the McLymont Fault Gold Zone. We successfully increased drilling efficiency and materially reduced our drilling cost per meter by moving our exploration base to the drive-in staging area at the Coast Mountain Hydroelectric Facility, on the southern margin of the property. We will endeavour to continue safe and cost-effective exploration as we advance the Burgundy Ridge copper gold porphyry target and work up our other prospective areas on the Newmont Lake Property.”
Highlights from the 2022 exploration program include:
- Logging of drill core from Burgundy Ridge identified wide zones of sulphide mineralization including chalcopyrite, bornite and chalcocite in several drill holes.
- Visual inspection of the core shows a strong correlation to the large chargeable geophysical anomaly identified using induced polarization geophysics (see March 9th, 2022, Enduro news release).
- Maiden drilling further west along the McLymont Fault Gold Zone target has shown that the area has been subject to intense hydrothermal activity, with multiple zones of quartz veining and sulphide mineralization visible in core.
-

Figure 1a: Plan view map of completed 2022 and historic drill holes at Enduro’s Burgundy Ridge alkalic copper-gold porphyry target. Source: Enduro Metals Corporation 
Figure 1b: Plan view map of completed 2022 and historic drill holes at Enduro’s McLymont West, along the McLymont Fault Gold Zone. Source: Enduro Metals Corporation
Exploration targets that were also explored in 2022 include:
- Chachi – the Company’s focus on Chachi has moved to the Southwest Ridge following drilling of the geophysical anomaly during 2021 which assisted in identifying a large 2,500m x 750m copper-gold anomaly further south of the drilled area. The Southwest Ridge anomaly is now the largest copper and gold in soil anomaly encountered on the Newmont Lake property to date, and shares similarities with the Burgundy System.
- North Toe – Geological prospecting of the North Toe zone has identified an area of quartz-chalcopyrite stockwork veining and encouraging porphyry-style alteration typical of alkalic copper-gold porphyry systems. The area is of comparable scale, and along strike of the Burgundy system. Similar to the work completed at Southwest Ridge, North Toe has strong similarities to the Burgundy copper-gold porphyry system, underlining a potential geological pattern of multiple porphyry centres within the Company’s 688km2 land package.
- NW Zone – Data interpretation is ongoing at the NW Zone to investigate further size and extent of the potentially expansive system. Drilling in 2022 has focused on the greater McLymont Fault Gold zone expanding the mineralized footprint of the system.
- Ken Zone – Mineralization and alteration indicative of an alkalic porphyry system has been encountered on surface through geological prospecting and planning is underway for potential future drilling.

Details of Property Expansion
The Company is also pleased to announce that it has acquired 100% interest in an additional 35km2 of mineral claims via staking on the eastern portion of the Newmont Lake Project, increasing the total land package to 688km2 (see Figure 2).
Source: Enduro Metals Corporation
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
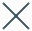
Silver Valley Metals Corp. (TSXV:SILV) has reported significant high-grade historical results that expand its Page Mine at depth at the Ranger-Page Project, in Silver Valley, Idaho. Silver Valley is a brownfield exploration company with two key projects comprising lithium-potassium in Zacatecas and San Luis Potosi, Mexico. The other main project for which results have been reported is the Range-Page silver-zinc-lead project in Idaho, USA.
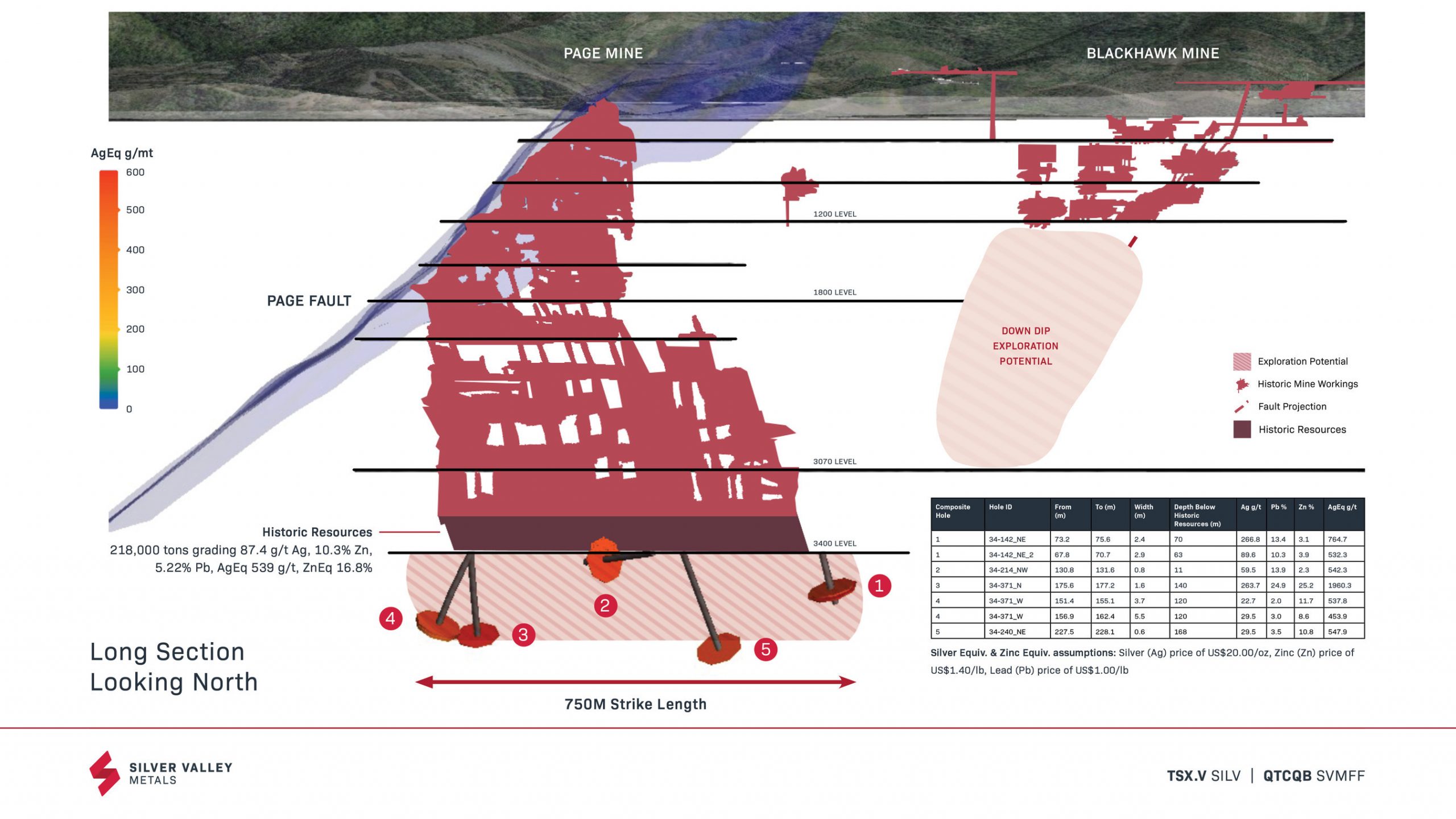
Highlights from the drilling are as follows:
- Drill hole 34-371_N intercepts 1,960 g/t silver equivalent* (264 Ag g/t, 25.2% zinc, 25.0% lead) over 1.60 metres
- Drill hole 34-142_NE intercepts 765 g/t silver equivalent* (267 Ag g/t, 3.1% zinc, 13.4% lead) over 2.4 metres and 532 g/t silver equivalent* (90 Ag g/t, 3.9% zinc, 10.3% lead) over 2.9 metres for a total of 5.3 metres of high-grade mineralization with these two intervals separated by 2.5 metres of negligible mineralization
- Drill hole 34-371_W intercepts 538 g/t silver equivalent* (23 Ag g/t, 11.7% zinc, 2% lead) over 3.7 metres and 454 g/t silver equivalent* (30 Ag g/t, 8.6% zinc, 3% lead) over 5.5 metres for a total of 9.2 metres of high-grade mineralization with these two intervals separated by 1.8 metres of negligible mineralization
- Drill hole intercepts range from 11 metres to 168 metres below the high-grade historic resources at the Page Mine (near true width)
- A top ten historical producer in the Silver Valley, the Page Mine was mined to approximately 806 metres below elevation over 44 years; with these historical drill results, Page remains open within high grade mineralization to near one kilometre below elevation extending the Page Mine’s depth by approximately 17%; or when considering past production, 7.5 years of historic production
- Over 750 metre strike length defined at depth
| * Silver Equiv. assumptions: Silver (Ag) price of US$20.00/oz, Zinc (Zn) price of US$1.40/lb, Lead (Pb) price of US$1.00/lb |
Page Mine Drill Results:
About: Ranger-Page project
Silver Valley’s primary focus is on its flagship Ranger-Page Project (“The Project”) located in the Silver Valley of Idaho, 60 kilometres east of Coeur d’Alene and 1 kilometre from the I-90 freeway. In 2020 Idaho was ranked the first in the world in policy perception and 9th best mining jurisdiction (Fraser Institute Annual Mining Survey). The Project borders the famous Bunker Hill Mine to the east and for the first time consolidates the western extent of the prolific Silver Valley mining corridor by one operator in the past 100+ years.
The Project is on patented claims, there are no royalties and comprise 6 historical mines. The largest of these, the Page Mine, was a top ten producer in the Silver Valley producing over 1 billion pounds of zinc and lead and 14.6 million ounces of silver. The Page Mine has high grade silver-zinc-lead historic reserves and remains wide open at depth beyond what has been defined to date.
There is shared underground infrastructure connecting the larger Page mine with five shallow historical mines within the larger Project area. The Company has underground mining data and surface geological data that supports high grade silver-zinc-lead mineralization present within the shallow, undeveloped mines. These mines remain open at depth, and laterally along strike.
Exploration potential beyond the historical mines is considered significant due to no modern systematic exploration applied to the project.
Source: Silver Valley Metals
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

BHP (ASX:BHP) is reportedly thinking about increasing its A$8.4 billion ($5.6 billion)offer for OZ Minerals Ltd. If they go through with this, it would mean that the leading miner in the world would have a bigger role in providing metals that are necessary for the transition to green energy sources.
In August, BHP rejected OZ Minerals’ first approach, claiming it undervalued the company’s prospects in precious metals like copper and nickel. On Friday, shares in OZ Minerals finished at A$25.25.
If this large acquisition goes through, it will be just one more in a series of big changes at the world’s biggest miner since Mike Henry became CEO in early 2020. The company has revived its interest in major deals, exited the oil and gas industry, and is pouring billions of dollars into a new potash mine in Canada.
According to the individuals, BHP may raise its A$25 per share offer for OZ Minerals as soon as this month. It wasn’t immediately clear what amount BHP would raise its bid, or whether OZ Minerals would accept a new offer from BHP.
Deliberations are ongoing and there’s no certainty that BHP will decide to return with a higher price, according to the people. A representative for BHP declined to comment, while a spokesperson for OZ Minerals couldn’t immediately be reached for comment outside regular business hours in Australia.
BHP’s strategies include diversifying into commodities that are linked to trends such as low-emissions travel and clean energy — particularly copper for solar power and nickel for lithium-ion batteries. It continues to be a major iron ore and steelmaking coal producer, as well as a significant iron ore miner, this year deciding to keep its last energy coal mine.
BHP has interests in mining copper along with OZ Minerals, which runs copper mines in South Australia, where BHP maintains its enormous Olympic Dam operation and Oak Dam prospect.
BHP’s desire to buy OZ Minerals is indicative of the company’s return to large-scale transactions, with its last major one being the $12.1 billion acquisition of Petrohawk Energy Corp. in 2011. However, it has made more modest purchases of copper and nickel assets since then.
Last year, the firm was defeated in its attempt to acquire nickel after losing a large sum of money on its six-month pursuit of Canadian miner Noront Resources Ltd., which was outbid by Australian billionaire Andrew Forrest.
The world’s largest producers are all optimistic about copper, anticipating increasing demand in cities and electric cars as the global economy decarbonizes. Rio Tinto Group reached a final agreement to acquire all remaining shares of Turquoise Hill Resources Ltd., which owns a large copper mine in Mongolia, earlier this month.
The long-term prospects for copper remain encouraging, but the metal’s price has plummeted dramatically since earlier this year, with concerns growing that Europe’s energy crisis, a tighter monetary policy by the Federal Reserve, and China’s Covid Zero plan will continue to weigh on demand.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Tertiary Minerals (LON:TYM) has signed a technical cooperation agreement with First Quantum Minerals (TSX:FM) to increase copper exploration in Zambia. This specific deal will include the Mukai and Mushima North project by Tertiary Minerals in the north-western province of Zambia. Mushima North is adjacent to First Quantum’s Trident project, including the Sentinel copper mine and the Enterprise nickel mine. Thanks to synergies between the properties and the new agreement, both companies will be able to boost copper exploration at the properties.
Executive Chairman Patrick Cheetham said in a statement: “This agreement will turbo-charge Tertiary’s Zambian exploration in these two key licence areas. We are set to benefit from FQM’s extensive and in-depth country experience, gained over many years of exploration and mine development in Zambia.”
Tertiary and First Quantum will establish a technical committee to work together to develop the two projects, which is located in an active exploration area for First Quantum. The Mushima North exploration licence is also in an active prospecting region for First Quantum. Tertiary and First Quantum will get together and form a technical committee to collaborate on the advancement of both initiatives.
First Quantum will also advise and assist Tertiary on the project’s technical matters and provide Tertiary with all of its historical exploration data for the two licence areas. The London-based miner said the agreement will provide them with the expertise of one of the world’s biggest copper producers, without any associated cost First Quantum. In return, Tertiary added, First Quantum will gain first-hand knowledge of new discoveries made and makes the company a future development partner thanks to the agreement.
Zambia is a focus for both companies, thanks to renewed confidence in the investment climate in the country. First Quantum had production of 435,000 tonnes of copper and 128,000 oz gold at Zambian operations in 2021, and the company approved a $1.25 billion expansion of the Kansanshi copper mine that aims to boost production further.
First Quantum has also recently approved a $100 million investment in the Enterprise nickel project that is expected to start producing in 2023 and is covered by the technical agreement. The company will ramp up production at the project with the goal of producing 30,000 tonnes of nickel concentrate per year.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
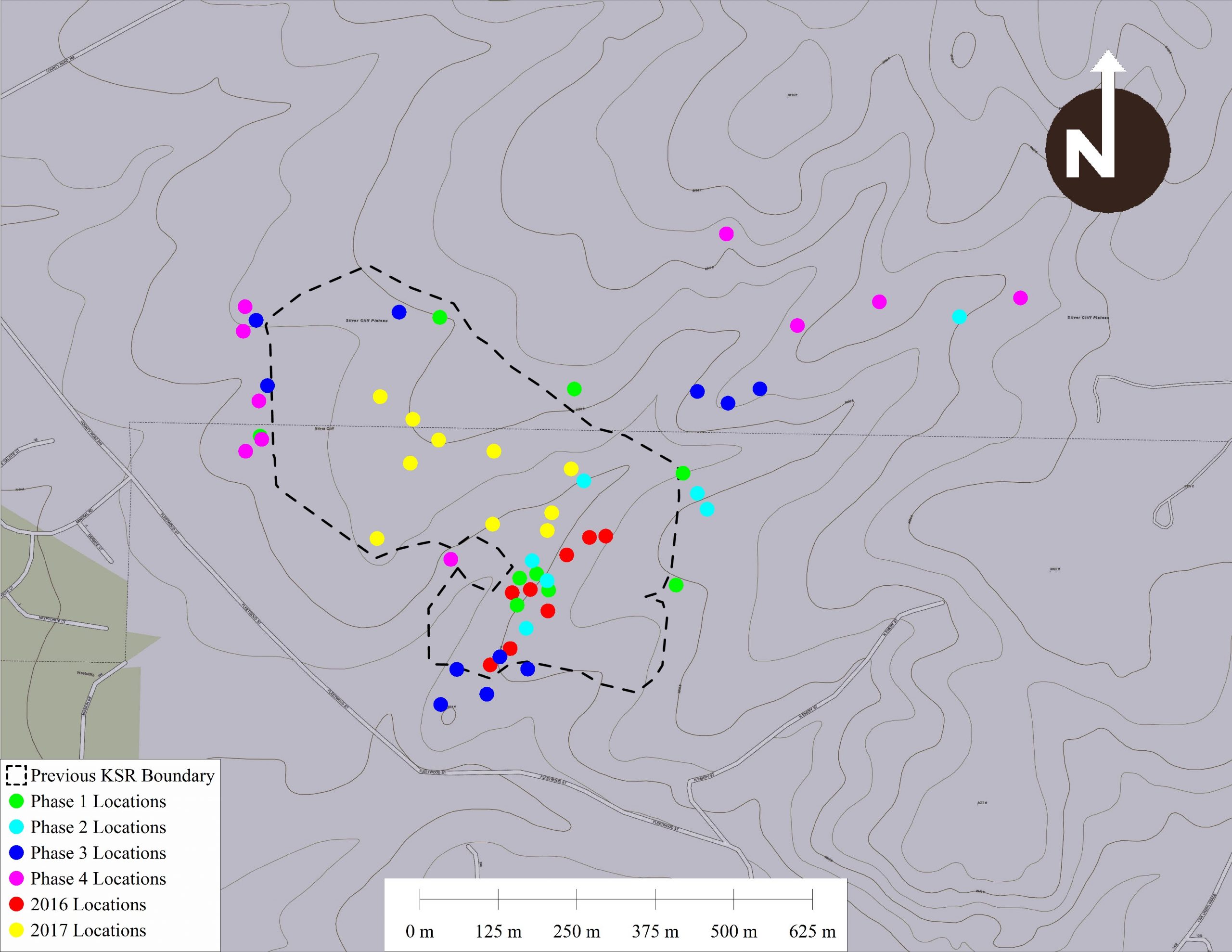
Viscount Mining (TSXV:VML) has announced the completion of its successful 4-phased step-out drill program at the Kate deposit, with a mineral resource estimate to follow shortly. Tenneco Minerals leased the property back in 1987, and had previous drill data available. Drilling had been done from 1968, and included results from 11,930 metre in 249 drill holes. Tenneco picked up the drilling with an additional 143 holes totally 7,949 metres. At that point, the company decided to construct a milling operation for the extraction of the silver reserves at Silver Cliff as an open pit mine.
Silver Cliff’s primary deposit was the Kate Silver Resource, with a historical estimate of 50M oz silver (not NI 43-101 compliant). Viscount took control of the property from Tenneco Minerals and started the first post-Tenneco drill program in 2106. The goal was to twin some of the historic drill holes at the Kate deposit with the highest-grade intercepts. Once the company received positive results from the program, ten more holes were twinned in 2017 in an area that was previously overlooked.
Viscount restarted drilling at the Kate in the fall of 2020. The primary goal of Phase 1 was to explore Arseneau’s 2018 assertion about the KSR boundary. Assay findings from holes including 20-03, which revealed 14.9 m of core testing over 703 G/T and 1.5 m testing at 3280 G/T, supported the necessity for a further inquiry into the high-grade zone within the KSR and defined an adjacent higher grade zone.
In 2021, the program moved from exploring higher-grade zone mineralization within a small area to looking at the southern limits of the KSR’s more advanced grade zone. Shortly after completion, soil sampling was undertaken as part of Phase 2’s study in the northeastern KSR. Hole 21-01 drilled during Phase 2 testing revealed 18.6 m of core testing over 147 G/T, with 1.5 m at 1010 G/T. This helped to define the KSR’s higher grade zone better while soil findings assisted in future drilling efforts by providing information on where best to drill.
In 2021, Phase 3 focused on the southward extension of the KSR higher grade zone. Drill holes were also drilled to the northeast and northwest of the existing KSR limits in order to evaluate promising soil sampling anomalies discovered during the previous phase. Positive drilling results from Phase 3 proved that the higher grade zone should be extended to the south, prompting further study on whether or how far to extend it to the north.
In the spring of 2022, we started Phase 4 which only had one goal: to explore if the ore body could expand in different areas. We placed most expansion holes near the West and Northeast boundary with one hole placed in the KSR gap.
Jacob Hooker, Silver Cliff Exploration Manager commented in a press release: “The Kate deposit was the first of 4 historical deposits at Silver Cliff to be drilled by Viscount. With historical information from the Kate being confirmed we will continue to step out the drilling to expand the higher grade zones. We have also been focusing on the historical Passiflora deposit with exciting news forthcoming.”
Jim MacKenzie Viscount CEO stated: “The overall results of the 4 phase drill program at the Kate has been very successful. We were able to confirm the hypothesis that there exists a higher-grade zone within the KSR that had been previously much ignored. Also, drilling has expanded the resource in 3 key directions that remain open to expansion. Now that all four phases are completed, our Independent Geologist is reviewing assays and analyzing the results along with the calculation of the data from the 46 additional holes drilled by Viscount since 2020. These results and selected historic drilling results will be included in an updated NI 43-101 to be released shortly. Our next phase of drilling at the Kate will include some areas to the North-North-West that have shown good potential combined with historical information, but has not been drill tested.”
Silver Cliff Exploration Manager Jacob Hooker commented: “Not only will these results help expand the silver resource, they also have great implications for inexpensive open-pit mining with most of the mineralization being immediately below the surface.”
Now that all four stages are completed, the company’s geologist is evaluating assays and analyzing the findings, as well as the data from Viscount’s 46 new holes drilled since 2020. An updated NI 43-101 will include these results and certain past drilling outcomes.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Canada’s Ivanhoe Mines (TSX:IVN) and Congo’s state mining company Gécamines have begun construction activities at the historic Kipushi underground zinc-copper mine, which they plan returning to production by late 2024. The two companies reached a key milestone this week with the commencement of development work on the project, located in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Ivanhoe has also concluded an agreement (MOU) with the provincial government of Haut-Katanga to investigate possibilities for extending border trade at the DRC-Zambia crossing in Kipushi, which will allow commercial goods and people to flow freely.
The company’s plan is to construct a commercial border outpost specifically for the Kipushi mine and update the existing one in Kipushi. As of now, it only serves people travelling between DRC and Zambia.
The companies formed a joint venture called Kipushi Corporation which had a breaking-ground ceremony for the project. The company noted pre-production capital costs estimated at $382 million which include contingency. At the moment, they will use existing rehabilitated surface and underground infrastructure to keep costs low. This plan is aimed at reducing the time to production to two years. The project includes a feasibility study which should include a 800,000 tonne-per-annum concentrator and an underground mine. Production for the mine is expected to be an average fo 240,000 tonnes of zinc per year, with a mine life of 14 years.
Both companies have noted that once the mine is in production, it has the potential to be the world’s highest-grade major zinc mine. Kipushi would have an average head grade of 36.4% for the first five years of production, head and shoulders above the nearest competing mine. The after-tax NPV of a zinc price at $1.40 per pound, with an 8% real discount rate, is $1.4 billion. The after-tax real internal rate of return (IRR) wold be 54% at those levels.
The mine is world-renowned for its production of copper and zinc. Union Minière operated the site for 42 years. In 1924, they started mining an 18% copper deposit from a surface open pit—which was the richest copper deposit at the time.
Kipushi then evolved into Africa’s biggest underground copper, zinc, and germanium mine. Gécamines took control of the facility in 1967 and ran it until 1993, when it was put on care and maintenance due to a variety of economic and political reasons.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
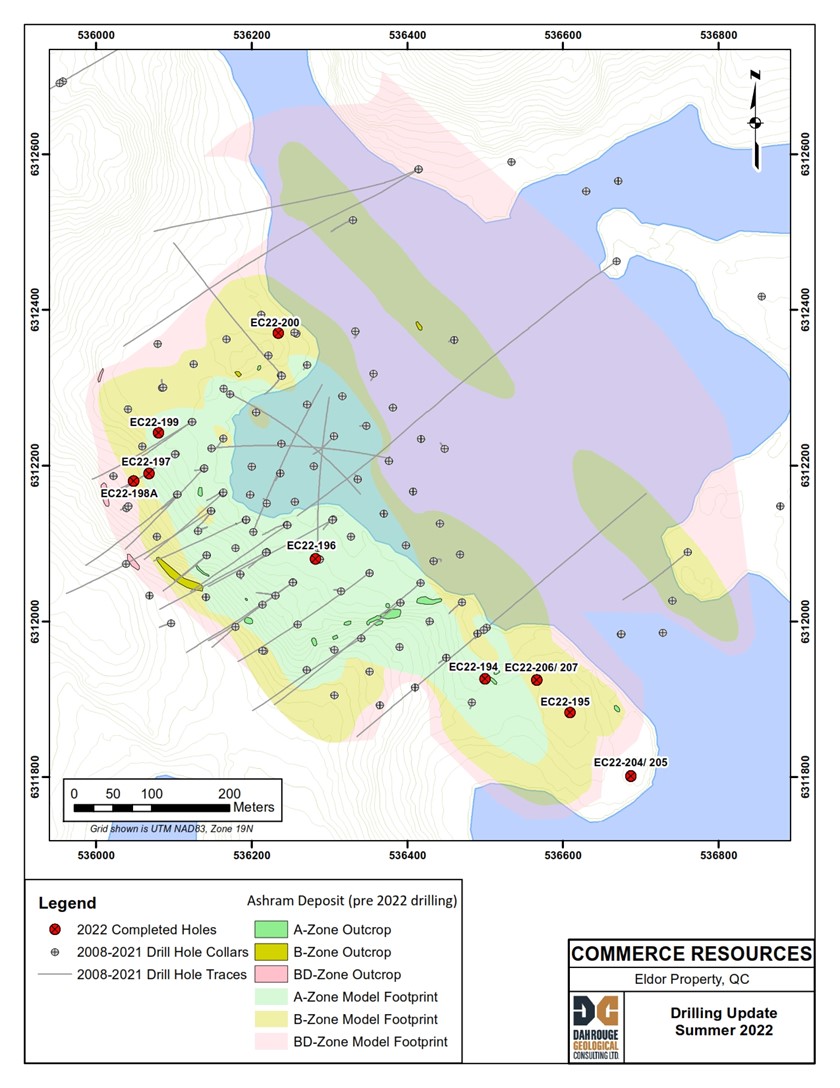
Commerce Resources (TSXV:CCE) has updated the 2022 drill program at the 100%-owned Ashram Rare Earth and Fluorspar Deposit in Quebec, Canada. The company has completed its final drill hole of the 2022 program at the Ashram Deposit, with a total of approximately 2,760 m drilled.
The holes were drilled – for delineation – at various orientations and locations with depths ranging from about 50 m to 410 m core length.
The 2022 drill core is currently being processed at the site, with samples collected and shipped to Activation Laboratories in Ancaster, ON for geochemical analysis. All analytical results are pending for the core samples from the 2022 program. As drilling holes are fully logged and sample analysis comes back, the geological model will be updated accordingly and further refined.
The objective of the 2022 drill hole plan, developed by our Prefeasibility Study consultant (BBA Inc.), is to infill a larger pit shell (~+50%) than what was considered in the Project’s 2012 Preliminary Economic Assessment. This larger pit shell is anticipated to support an initial mineral reserve estimate upon completion of the Prefeasibility Study for the Project.

Highlights of the program are as follows:
The first two (2) drill holes (EC22-194 and 195) were completed as step-outs at the southern end of the deposit to improve the confidence of the geological model in this area and extended the mineralized footprint at Ashram an additional ~100 m to the southeast (see news release dated August 12th, 2022). An additional four (4) drill holes (EC22-204, 205, 206, and 207) were completed at the southern end of the deposit to further constrain the geological model and probe the deposit’s southern contact. The remaining six (6) drill holes (EC22-196, 197, 198, 198A, 199, and 200) were completed as resource infill with the objective of increasing confidence from the inferred/indicated categories to the indicated/measured categories within the anticipated Prefeasibility pit shell where the neodymium-praseodymium (“NdPr”) contents are highest. Depending on the location within the deposit, the NdPr distribution – i.e. % of Nd+Pr oxide of the total rare earth oxide (“REO”) – typically varies from 21-24+% with monazite being the dominant carrier of the rare earth elements (“REEs”).
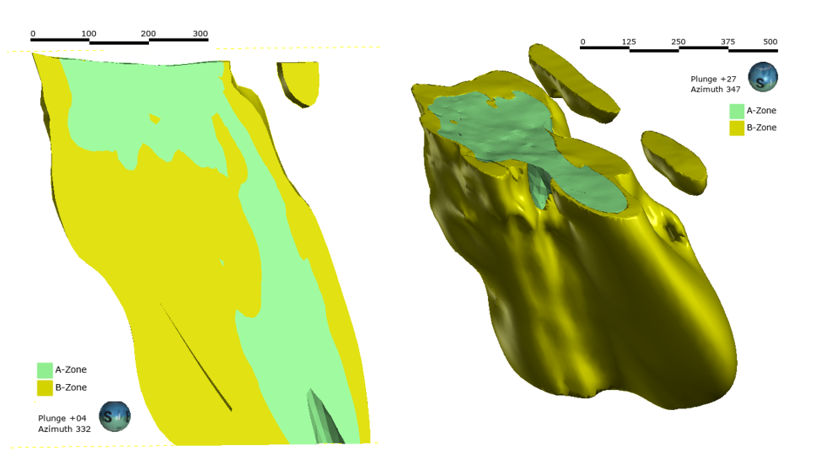
About the Ashram Deposit
The Ashram Deposit ranks as one of the largest REE (and fluorspar) deposits globally, consisting of a monazite dominated, single mineralized body outcropping at surface, and has a footprint approximately 700 m along strike, over 300 m across, and 600 m deep, remaining open in several directions. The deposit hosts a measured resource of 1.6 million tonnes (Mt) at 1.77% rare earth oxide (REO) and 3.8% F, an indicated resource of 27.7 Mt at 1.90% REO and 2.9% F, and an inferred resource of 219.8 Mt at 1.88% REO and 2.2% F, at a cut-off grade of 1.25% REO (Effective Date July 5th, 2012). Note, mineral resources are not mineral reserves as they do not have demonstrated economic viability. There is no certainty that all or any part of the Mineral Resources will be converted into Mineral Reserves.
Source: Commerce Resources Corp.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
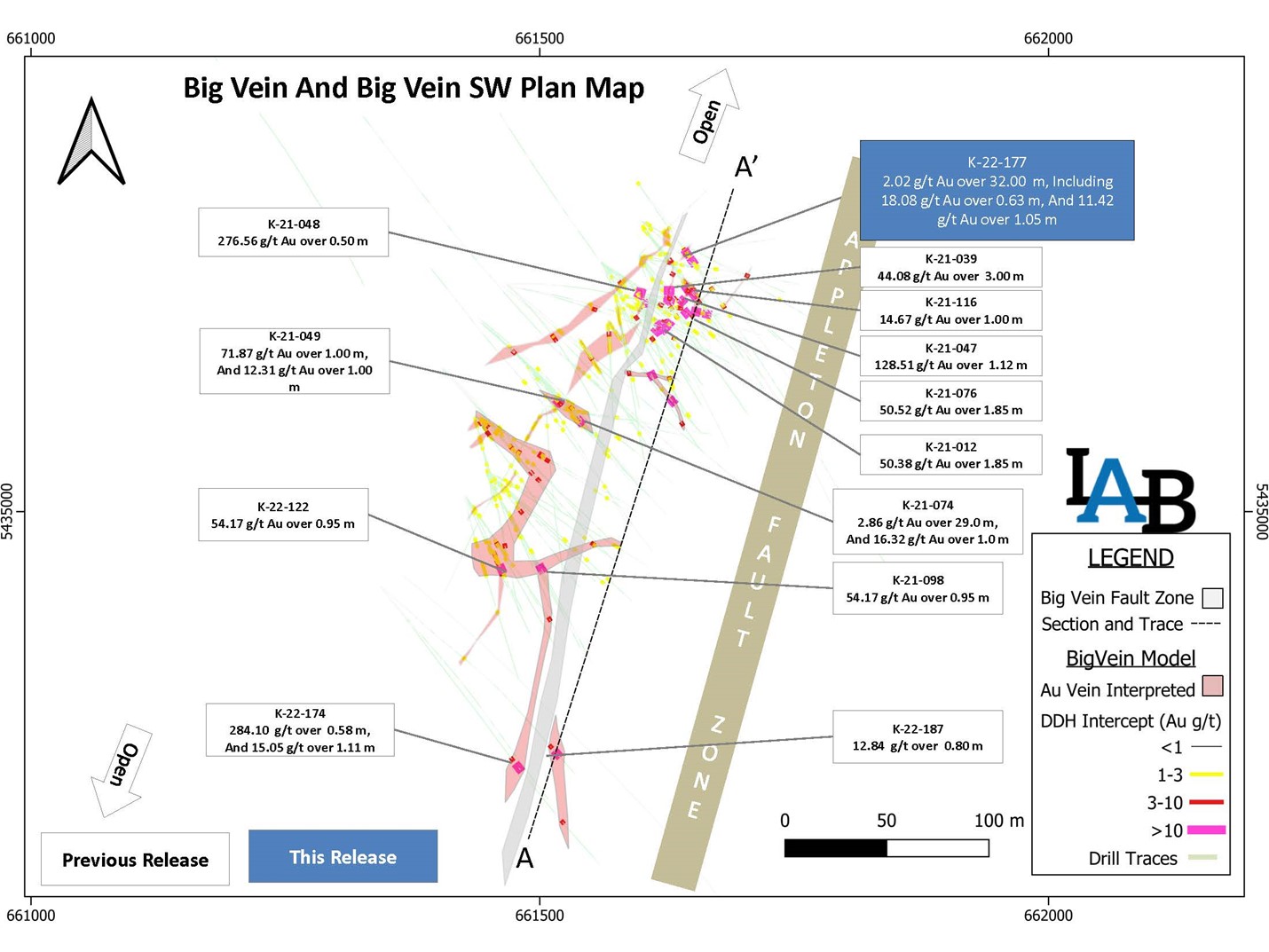
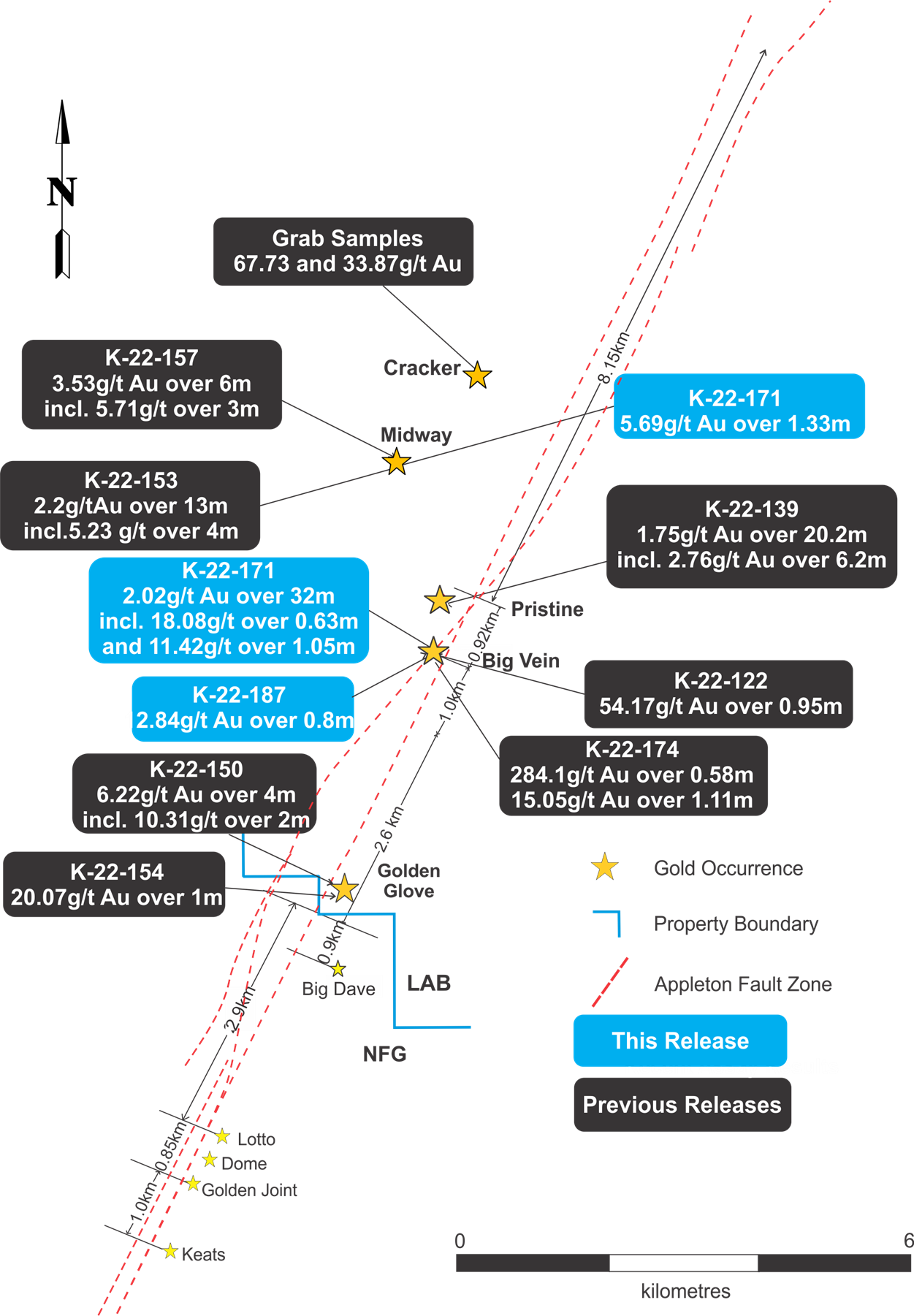
Labrador Gold (TSXV:LAB) has announced new results from ongoing drilling targeting the Appleton Fault Zone over a 12-kilometre strike length at the 100% owned Kingsway Project. the
Highlights of the drilling include an intersection of 2.02 g/t Au over 32 metres from 134 metres that included 18.08 g/t Au over 0.63 metres and 11.42 g/t Au over 1.05 metres in Hole K-22-177 from the north end of Big Vein. The intersection is approximately 75 metres north of the discovery outcrop. In addition, Hole K-22-187 at Big Vein southwest intersected 12.84 g/t Au over 0.8 metres from 341 metres.
The last results from initial drilling at Midway showed an intersection of 5.69 g/t Au over 1.33 metres in Hole K-22-171. Further drilling is planned at Midway to test the continuity of gabbro-hosted mineralization along strike towards Cracker.
Labrador Gold is a Canadian-based mineral exploration company focused on Eastern Canada. The Kingsway Project is the flagship project for the company, associated with gold occurrences in the area including the occurrences immediately to the south of the Kingsway project found by New Found Gold.
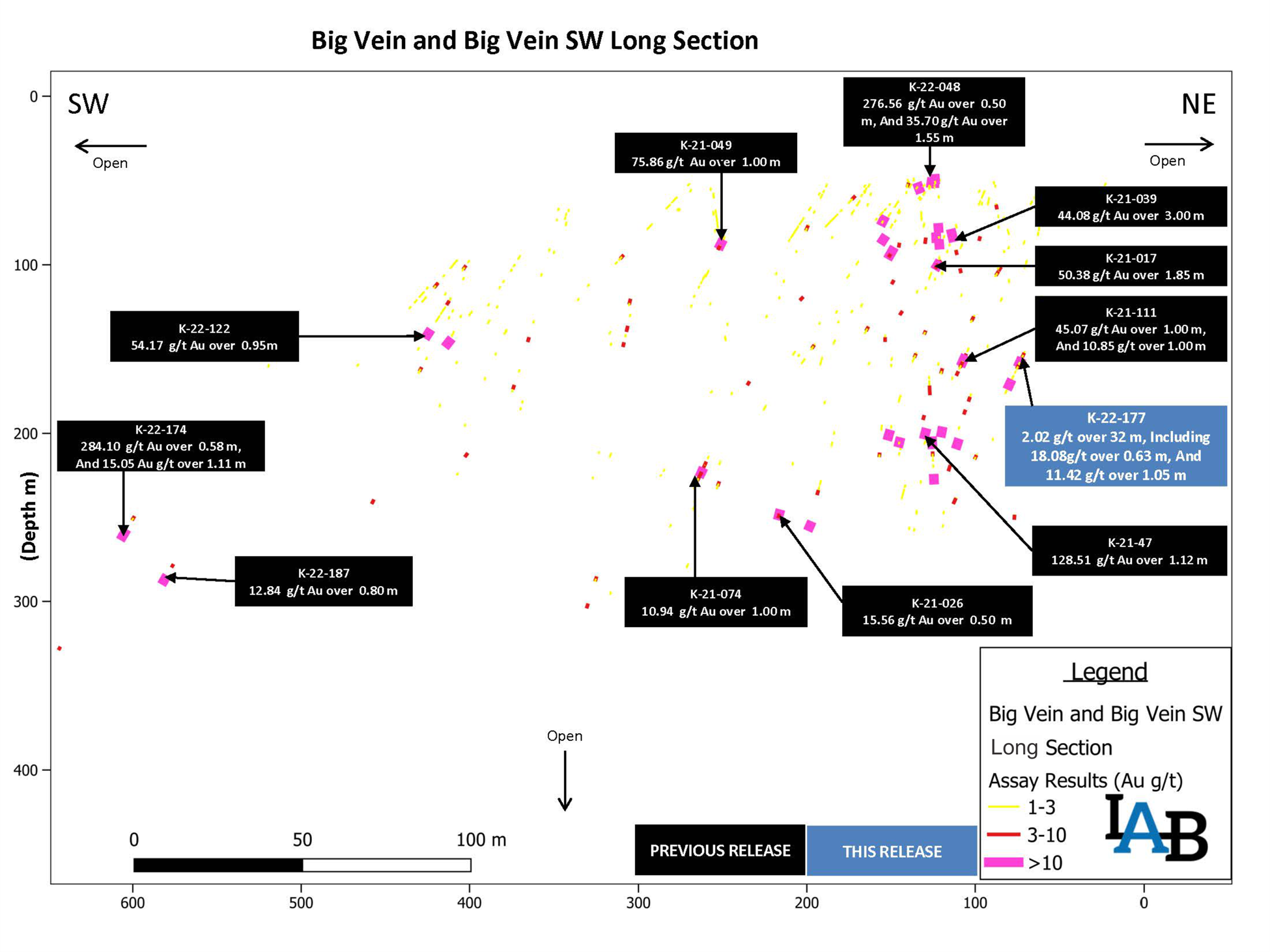
Roger Moss, President and CEO of Labrador Gold, commented in a press release: “Drilling at Big Vein continues to deliver excellent results with the longest mineralized intersection of 32 metres grading 2.02 g/t gold drilled on the property to date. We are currently testing this intersection down dip. The intersection is approximately 30 metres north of another long intercept of 6.07 g/t Au over 19m in hole K-21-111. Big Vein has now been drilled over a strike length of approximately 520 metres and remains open both to the northeast and southwest. Two rigs continue drilling at Big Vein to test for extensions of the mineralization in both directions.”
Highlights from the results are as follows:
- Hole K-22-177 intersected 2.02 g/t Au over 32 metres including 18.08 g/t Au over 0.63 metres and 11.42 g/t Au over 1.05 metres.
- Mineralization at Big Vein remains open along strike to the southwest and northeast.
- Drilling also intersected high-grade mineralization at Big Vein southwest grading 12.84 g/t Au over 0.8 metres.
| Hole ID | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Au (g/t) | Zone |
| K-22-187 | 157.80 | 158.25 | 1.20 | 1.08 | Big Vein SW |
| 328.55 | 328.85 | 0.30 | 3.27 | ||
| 341.00 | 341.80 | 0.80 | 12.84 | ||
| K-22-184 | 140.26 | 140.59 | 0.33 | 2.89 | Big Vein SW |
| 336.25 | 337.89 | 1.64 | 2.69 | ||
| K-22-180 | nsv | CSAMT | |||
| K-22-179 | 72.00 | 72.76 | 0.76 | 1.08 | Golden Glove |
| K-22-178 | nsv | Big Vein SW | |||
| K-22-177 | 8.00 | 9.00 | 1.00 | 1.01 | Big Vein |
| 93.74 | 94.55 | 0.81 | 1.11 | ||
| 134.00 | 166.00 | 32.00 | 2.02 | ||
| including | 142.77 | 143.40 | 0.63 | 18.08 | |
| and | 158.95 | 160.00 | 1.05 | 11.42 | |
| 212.00 | 215.00 | 3.00 | 2.63 | ||
| 245.00 | 248.00 | 3.00 | 3.60 | ||
| 265.00 | 266.00 | 1.00 | 1.73 | ||
| K-22-176 | nsv | Golden Glove | |||
| K-22-175 | 63.00 | 65.00 | 2.00 | 1.48 | Big Vein |
| 230.00 | 232.00 | 2.00 | 2.87 | ||
| K-22-174 | 296.00 | 297.49 | 1.49 | 3.65 | Big Vein SW |
| 407.00 | 407.30 | 0.30 | 3.24 | ||
| K-22-173 | 11.00 | 12.00 | 1.00 | 1.04 | Big Vein |
| 16.00 | 17.00 | 1.00 | 1.38 | ||
| 50.00 | 51.00 | 1.00 | 2.23 | ||
| K-22-172 | nsv | CSAMT | |||
| K-22-171 | 194.50 | 198.00 | 3.50 | 1.44 | Midway |
| 201.17 | 202.50 | 1.33 | 5.69 | ||
| K-22-170 | 11.00 | 12.00 | 1.00 | 1.10 | HTC |
| 35.00 | 44.00 | 9.00 | 1.42 | ||
| 218.00 | 219.00 | 1.00 | 1.01 | ||
| K-22-169 | nsv | Golden Glove | |||
| K-22-168 | 165.91 | 166.21 | 0.30 | 1.01 | Midway |
| 217.90 | 218.40 | 0.50 | 1.82 | ||
| K-22-167 | 57.00 | 62.00 | 5.00 | 1.90 | Big Vein |
| K-22-166 | nsv | Midway | |||
| K-22-165 | 243.00 | 244.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | Golden Glove |
Table 1. Summary of assay results. All intersections are downhole length as there is insufficient Information to calculate true width.
A total of 52,648 metres have been drilled to date out of the planned 100,000 metre program. Assays are pending for samples from approximately 3,343 metres of core (11% of the total submitted).
Drilling at Kingsway continues with four drill rigs, two working at Big Vein, one at Golden Glove and one at the CSAMT target. Ongoing detailed till sampling and prospecting continues to generate new drill targets along the Appleton Fault Zone and the gabbro trend north and south of Midway. Drilling will begin on these targets once initial drilling at CSAMT is complete.
The Company has $23.6 million in cash and is well funded to carry out the remaining 47,000 metres of the planned drill program as well as further target generation on the property.
| Hole ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Azimuth | Dip | Total depth |
| K-22-187 | 661343.8 | 5434926 | 44.151 | 130 | 50 | 374 |
| K-22-184 | 661343.9 | 543496.4 | 44.481 | 130 | 45 | 428 |
| K-22-180 | 666592.3 | 5443605 | 46.42 | 140 | 45 | 278 |
| K-22-179 | 660543 | 5431776 | 45.79 | 320 | 45 | 401 |
| K-22-178 | 661343 | 5434926 | 44.352 | 140 | 50 | 404 |
| K-22-177 | 661594 | 5435327 | 45.7 | 145 | 50 | 826 |
| K-22-176 | 660541 | 5431776 | 45.857 | 290 | 45 | 401 |
| K-22-175 | 661598 | 5435287 | 51.683 | 120 | 57.5 | 308 |
| K-22-174 | 661343.3 | 5434926 | 44.289 | 140 | 45 | 476 |
| K-22-173 | 661599.9 | 5435287 | 51.001 | 120 | 55 | 93 |
| K-22-172 | 666591.7 | 5443606 | 46.42 | 310 | 45 | 278 |
| K-22-171 | 661254.7 | 5437924 | 78.349 | 140 | 45 | 247 |
| K-22-170 | 661599.9 | 5435286 | 51.096 | 120 | 45 | 299 |
| K-22-169 | 660627.7 | 5431879 | 44.55 | 280 | 55 | 401.44 |
| K-22-168 | 661255.8 | 5437937 | 77.432 | 310 | 45 | 264.75 |
| K-22-167 | 661599.3 | 5435286 | 51.32 | 130 | 55 | 296 |
| K-22-166 | 661202.7 | 5437880 | 77.473 | 140 | 45 | 260 |
| K-22-165 | 660626 | 5431881 | 44.596 | 280 | 45 | 398 |
Table 2. Drill hole collar details
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
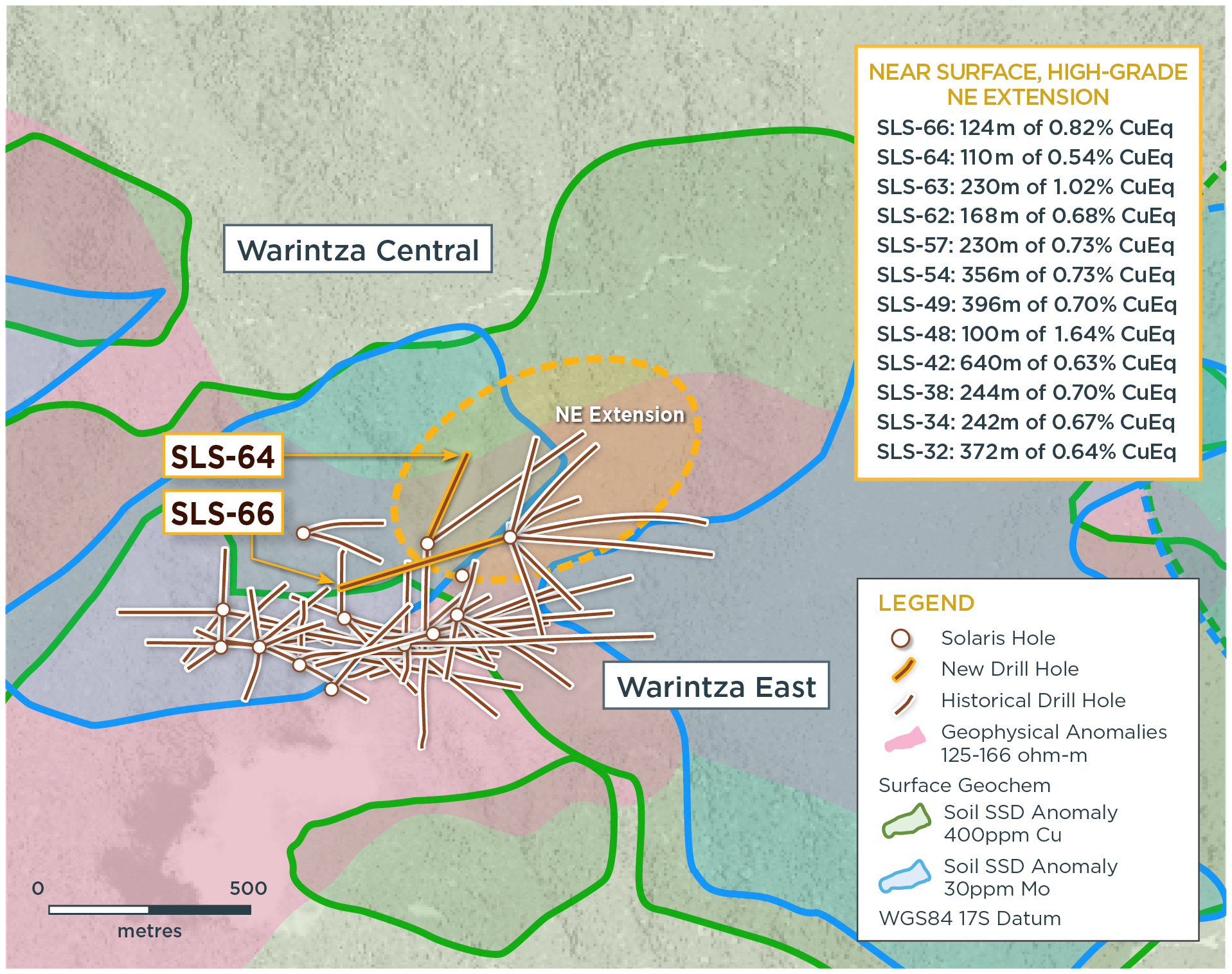
Solaris Resources (TSX:SLS) has reported new assay results from a series of holes at the Warintza Project in southeastern Ecuador. The holes are aimed at growing the Northeast Extension of the previously announced “Indicative Starter Pit”. The company is moving forward with drilling platforms in the Northeast Extention that are set to drive the latest high-grade results from the project.
Mr. Jorge Fierro, Vice President of Exploration, commented in a press release: “Drilling from existing and recently-completed platforms in the Northeast Extension zone is a key driver in the expansion of the ‘Indicative Starter Pit’, and we look forward to reporting the next set of results in the near future as the backlog of assays pending is now resolved.”
The “Indicative Starter Pit” was noted in an April 18, 2022 announcement from the company in a mineral resource estimate for the Warintza Central Deposit, in which the company reported in-pit resources of 579 Mt at 0.59% CuEq (Ind) and 887 Mt at 0.47% CuEq (Inf), and 180 Mt at 0.82% CuEq (Ind) and 107 Mt at 0.73% CuEq (Inf) for the “Indicative Starter Pit”.
Solaris also intends to spin out its non-core assets in Ecuador outside of the Warintza porphyry cluster, Peru, Chile, and Mexico into a new incorporated wholly-owned subsidiary of Solaris named Solaris Exploration Inc. Following the internal re-organization, it is expected that 100% of the common shares of Solaris Exploration Inc. will be spun out to shareholders of Solaris relative to their shareholdings.
Figure 1 – Plan View of Warintza Central Drilling Released to Date
Highlights from the results are as follows:
Additional drilling has expanded the Northeast Extension of the ‘Indicative Starter Pit’ recently estimated at 180 Mt at 0.82% CuEq¹ (Indicated) and 107 Mt at 0.73% CuEq¹ (Inferred) within the Warintza Mineral Resource Estimate² (“MRE”). This zone is characterized by near surface, high-grade mineralization and remains open for further growth with follow-up drilling underway.
- SLS-66 was collared on a platform at the northeastern limit of the Warintza Central grid and drilled southwest into an open volume, returning 124m of 0.82% CuEq¹ within a broader interval of 622m of 0.42% CuEq¹ starting from surface
- SLS-66 follows from previous holes SLS-63 and SLS-54, which were drilled from the same pad to the north and southeast and respectively returned high-grade intervals of 230m of 1.02% CuEq¹ and 356m of 0.73% CuEq³ within broader intervals (refer to press releases dated Jul 20, 2022 and Apr 4, 2022 for details)
- SLS-64 was collared on a platform at the northern limit of Warintza Central and drilled north-northeast into an open volume, returning 110m of 0.54% CuEq¹ from near surface within a broader interval of 440m of 0.48% CuEq¹, extending and broadening the zone to the north in this area
- SLS-64 follows from previous holes SLS-62 and SLS-48, which were drilled from the same pad to the northeast and south and respectively returned high-grade intervals of 168m of 0.68% CuEq¹ and 100m of 1.64% CuEq³ within broader intervals (refer to press releases dated Jul 20, 2022 and Feb 28, 2022 for details)
- SLS-65, which is a step out hole from a new platform 200m to the north, has now been completed after operational delays with adjustments to the platform for drilling and assays are expected within the next four weeks
Table 1 – Assay Results
| Hole ID | Date Reported | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Cu (%) | Mo (%) | Au (g/t) | CuEq¹ (%) |
| SLS-66 | Sep 07, 2022 | 0 | 622 | 622 | 0.32 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.42 |
| Including | 66 | 190 | 124 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.82 | |
| SLS-64 | 78 | 518 | 440 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.48 | |
| Including | 78 | 188 | 110 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.54 |
Notes to table: True widths of the mineralized zone are not known at this time.
Table 2 – Collar Location
| Hole ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation (m) | Depth (m) | Azimuth (degrees) | Dip (degrees) |
| SLS-66 | 800383 | 9648303 | 1412 | 689 | 255 | -48 |
| SLS-64 | 800178 | 9648285 | 1439 | 571 | 26 | -66 |
Notes to table: The coordinates are in WGS84 17S Datum.
Endnotes
- Copper-equivalence calculated as: CuEq (%) = Cu (%) + 4.0476 × Mo (%) + 0.487 × Au (g/t), utilizing metal prices of US$3.50/lb Cu, US$15.00/lb Mo, and US$1,500/oz Au, and assumes recoveries of 90% Cu, 85% Mo, and 70% Au based on preliminary metallurgical test work.
- Refer to Solaris’ technical report titled, “NI 43-101 Technical Report for the Warintza Project, Ecuador” with an effective date of April 1, 2022, prepared by Mario E. Rossi and filed on the Company’s SEDAR profile at www.sedar.com.
- Copper-equivalence calculated as: CuEq (%) = Cu (%) + 3.33 × Mo (%) + 0.73 × Au (g/t), utilizing metal prices of US$3.00/lb Cu, US$10.00/lb Mo, and US$1,500/oz Au. No adjustments were made for recovery prior to the updated Warintza Mineral Resource Estimate, as the metallurgical data to allow for estimation of recoveries was not yet available. Solaris defined CuEq for reporting purposes only.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
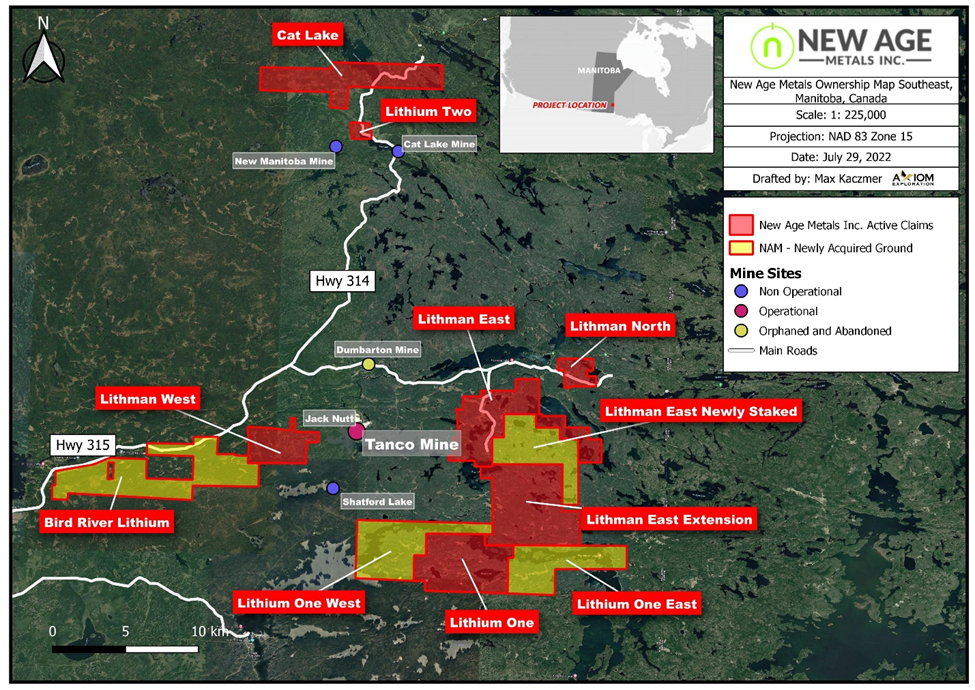
New Age Metals (TSXV:NAM) has announced that on September 1, 2022 it commenced its maiden drill program at its Lithium One Project in Southeastern Manitoba. The property is located in the Winnipeg River Pegmatite Field known for the numerous Li-bearing pegmatite showings.
Critical to the project is the active exploration agreement the company has with the Sagkeeng First Nation. New Age will work with members of Sagkeeng throughout the project. Sagkeeng will be an important partner in consultation with New Age Metals to ensure that the project is carried out with respect to local needs.
Figure 1: White spodumene blades in a matrix of lepidolite (Lithium Mica) from the Silverleaf showing. Spodumene blades can reach a length of up to 40 centimetres and a width of 10 centimeters.

The Lithium One Property is part of the world-renowned Tanco Pegmatite, which has been mined for Tantalum, Cesium, and Lithium in varying amounts since 1969. The historic presence of several surface Pegmatites of various sizes and compositions in the area surrounding the Lithium One Project has made it famous for its Silver Leaf Pegmatite.
The planned drilling program’s focus is to target the down-dip extension and lateral continuity of the Silverleaf Pegmatite. This will be done with 10 drill holes that go 150 meters deep at surface. The targeting has been better defined by 3D modelling historic drill results as well as newly acquired airborne gradient magnetics data.
The Silverleaf Pegmatite is a highly fractionated Lithium-bearing Pegmatite that dips shallowly. Shallow diamond drilling and trenching have been used to explore the deposit for approximately 170 meters on either side of strike, with a maximum width of about 30 m. The lepidolite-spodumene (lithium-bearing) zone outcrops as three large masses individually up to 23 x 6 m in size.
The open pit began in the late 1920s, when a substantial sample of spodumene was dug from the southwest side of the Silverleaf Pegmatite. Due to fluctuations in market conditions and commodity rates, large-scale mining operations were not attempted at that time.
Figure 2: New Age Metals land holdings, Southeast Manitoba
New Age Metals is a junior mineral exploration and development company with two divisions: Platinum Group Metals & Lithium/Rare Element. Based in North America, their green metal projects have the potential to make a large impact in the near future, and beyond.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
Québec Nickel Corp (CSE:QNI) has announced new assay results from drilling completed at the Fortin Sill Zone, located 80 kilometers northeast of Val-d’Or, Québec. Drilling showed 35.6 metres grading 0.59% nickel, 0.54% copper, 238 parts per million cobalt, 0.44 gram platinum per tonne, 0.42-gram palladium and 0.15-gram gold starting from 11.7 metres depth in step-out hole QDG-22-29.
Furthermore, the Vancouver-based mineral exploration company announced assay results from the Fortin Sill discovery outcrop channel sampling program that was completed this summer. Quebec Nickel SA said that 9,000m in 36 drill holes had been completed at the Ducros project, all of which were done in the eastern section.
Highlights from the step-out drilling are as follows:
- Magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulphides encountered in two new holes collared to the southeast of the Fortin Sill Zone discovery outcrop.
- Hole QDG-22-28 cored through a 29.90 metre interval averaging 0.30% Ni, 0.31% Cu, 167 ppm Co, and 0.45 g/t Pt-Pd-Au which includes a higher-grade subinterval containing 0.46% Ni, 0.64% Cu, 209 ppm Co and 0.72 g/t Pt-Pd-Au over 3.24 metres.
- Hole QDG-22-29 intersected a 11.80 metre interval containing 1.44% Ni, 1.49% Cu, 461 ppm Co and 2.79 g/t Pt-Pd-Au which includes a higher-grade subinterval assaying 1.85% Ni, 1.65% Cu (3.50% Ni + Cu), 576 ppm Co and 3.27 g/t Pt-Pd-Au over 8.43 metres.
- A new permit application has been delivered to the Québec Government that will allow for additional expansion drilling of the Fortin Sill Ni-Cu-Co-PGE-Au zone.
Highlights from the Fortin Sill discovery outcrop channel sampling are as follows:
- Channel 2 results: 1.30% Ni + Cu, 179 ppm Co, 1.39 g/t Pt-Pd-Au over 13.00 metres including 1.60% Ni + Cu, 178 ppm Co, 2.02 g/t Pt-Pd-Au over 7.16 metres.
- Channel 5 results: 1.08% Ni + Cu, 207 ppm Co, 1.26 g/t Pt-Pd-Au over 14.45 metres.
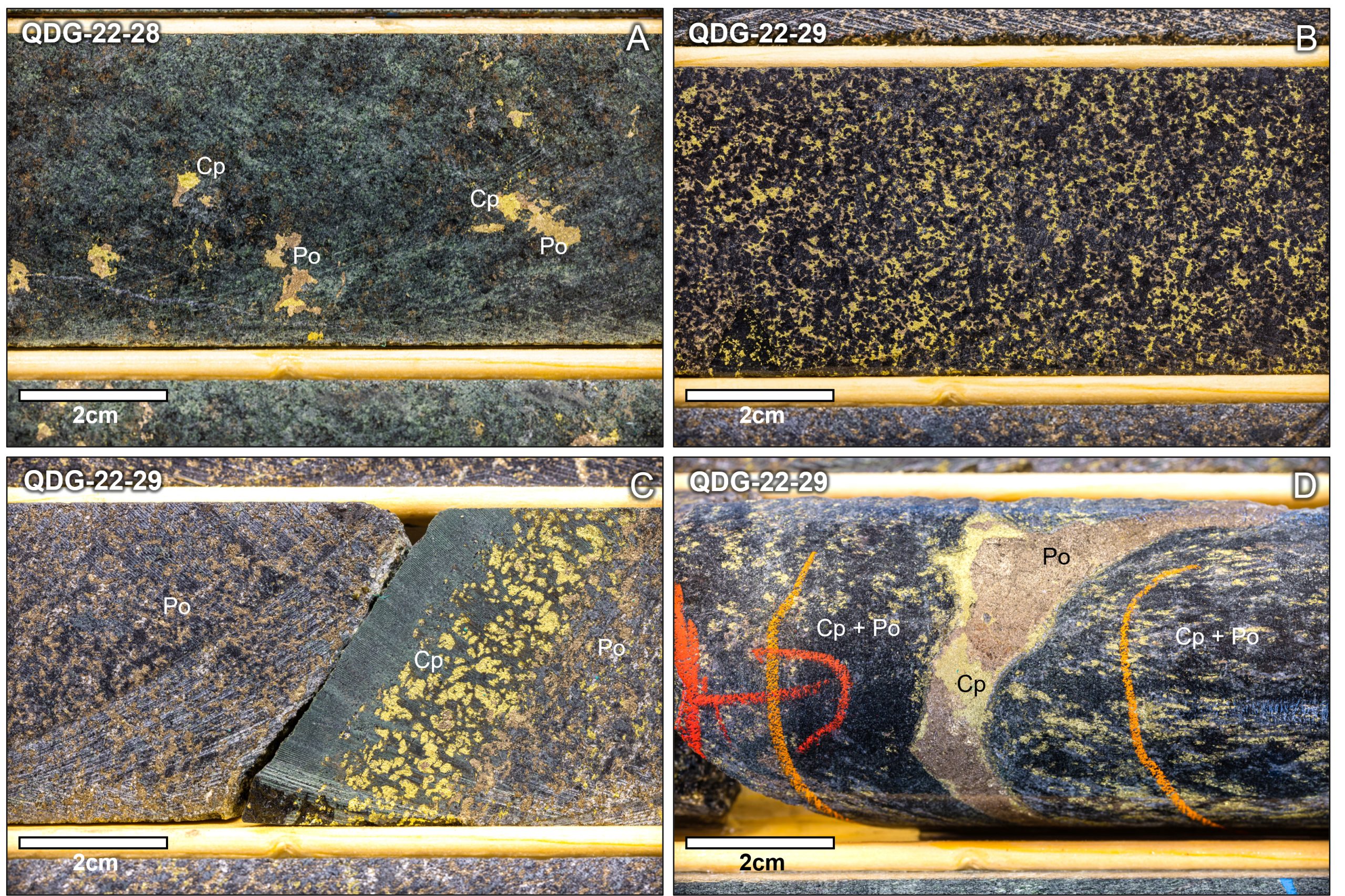
The firm said that the results from channel samples collected at the Fortin Sill discovery outcrop in June have been received. The work was completed to verify the results of a limited channel sampling program that was conducted by Golden Valley Mines at the Fortin Sill showing in 2007.
Québec Nickel’s Ducros property is located in the eastern portion of the Abitibi Greenstone Belt and consists of 280 contiguous mining claims covering 15,147 hectares. The company has also submitted a new permit application to the Québec government for permission to create additional access trails and drilling pads. These will be located adjacent to and along the interpreted strike of the Fortin Sill Zone. Additionally, this will allow for expansion drilling at the nickel-copper-cobalt-PGE-gold zone.
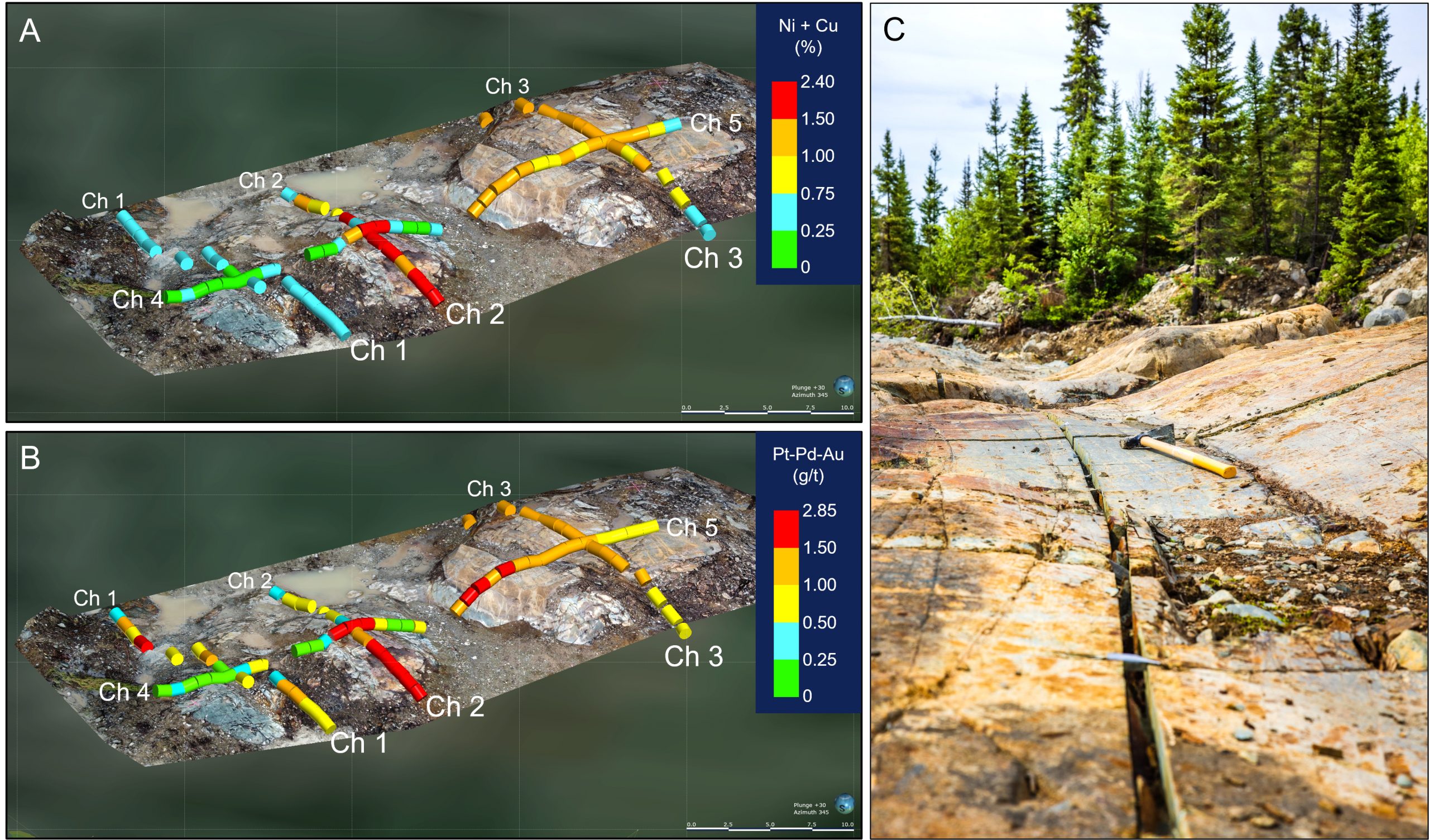
Alongside the diamond drilling and channel sampling, a property-wide biogeochemistry survey is being undertaken which will be used to improve future drill targets. Up until now, over 800 black spruce bark samples have been taken and put forward to ALS Global’s analytical laboratory in Vancouver.
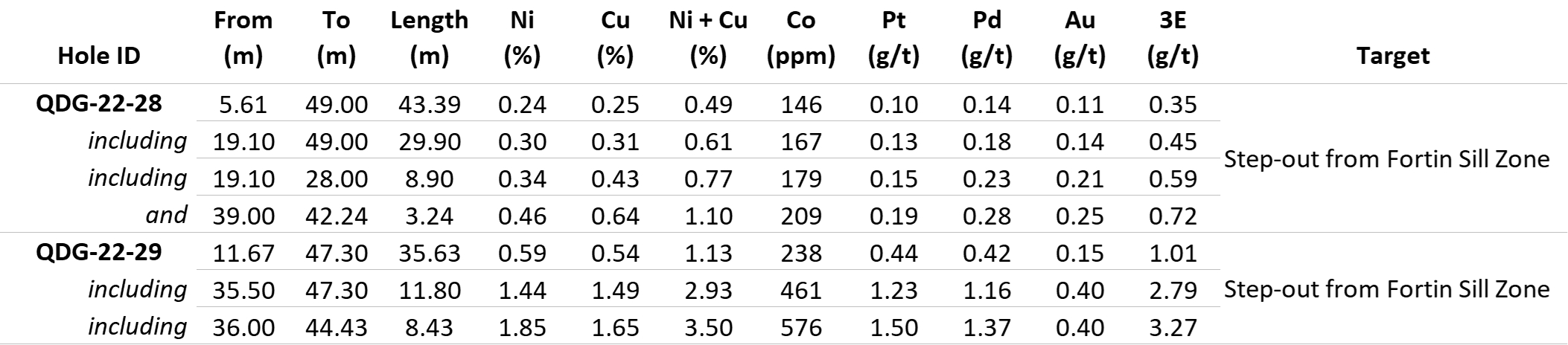
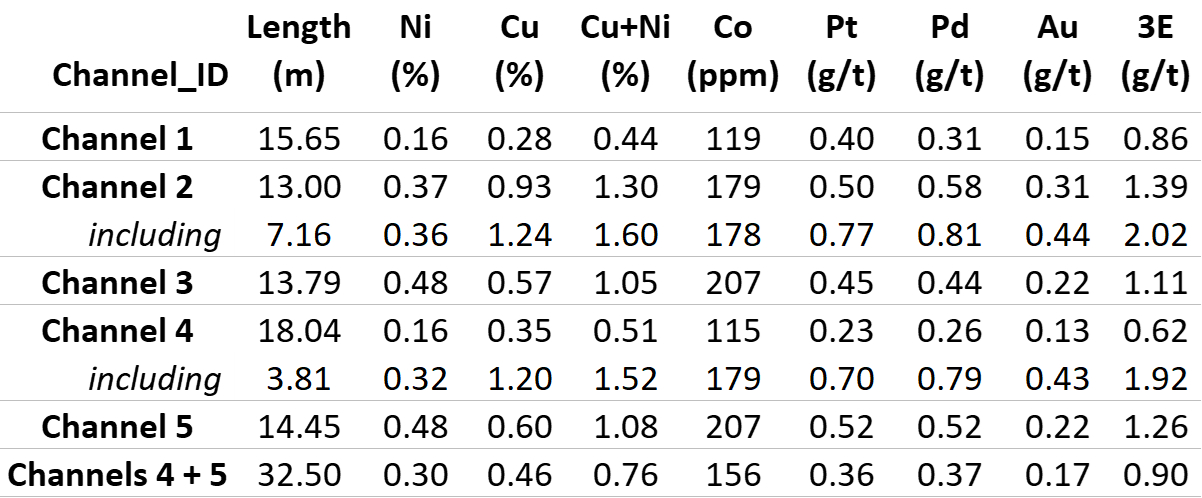
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
If you would like to receive our free newsletter via email, simply enter your email address below & click subscribe.
CONNECT WITH US
Tweets
Tweet with hash tag #miningfeeds or @miningfeeds and your tweets will be displayed across this site.
MOST ACTIVE MINING STOCKS
Daily Gainers
 Lincoln Minerals Limited Lincoln Minerals Limited |
LML.AX | +125.00% |
      |
GCR.AX | +33.33% |
      |
CASA.V | +30.00% |
      |
AHN.AX | +22.22% |
      |
ADD.AX | +22.22% |
      |
AZM.V | +21.98% |
      |
NSE.V | +21.05% |
      |
DYG.V | +18.42% |
      |
AAZ.V | +18.18% |
      |
GLA.AX | +17.65% |



 Follow us on Twitter
Follow us on Twitter Become our facebook fan
Become our facebook fan