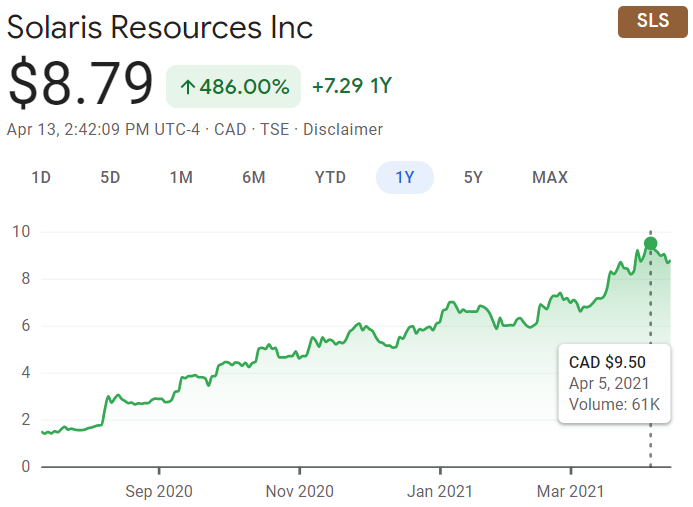
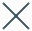
The recent election in Ecuador, held on October 15, 2023, was a major moment not just in the country’s politics but also for its economic health, particularly the mining sector. Daniel Noboa, the newly elected president, is the son of a well-known banana magnate and his win is widely regarded as a favourable development for the mining industry. He defeated his opponent in a political climate that had investors, both domestic and international, keeping a watchful eye on the possible effects on extractive industries in the country.
Focus on Extractivism in the New Administration
The Noboa administration is anticipated to lay a strong emphasis on extractivism during the first 100 days in office. Extractivism is an economic model based on the principle that the exploitation of natural resources like oil, gas, and minerals is crucial for national development. Ecuador is a nation rich in these resources, boasting some of Latin America’s most significant deposits of gold, silver, and copper. Noboa’s approach aligns well with this wealth, fostering a setting that could fuel economic growth through natural resource extraction, and he has placed this at the forefront of his plan to close the fiscal deficit in the country.
From 2018 to 2020, Canada spearheaded foreign direct investment (FDI) in Ecuador, with a focus on large-scale mining projects. Mining is one of the key industries in Ecuador, and this trend of foreign investment is likely to continue, perhaps even more so under Noboa’s pro-business administration. His win comes at a critical juncture when four major mining projects are slated to begin production by the end of 2025, initially set into motion during the term of his predecessor, Guillermo Lasso.
Though there is plenty of optimism, it’s important to note that the mining sector in Ecuador is not without its hurdles. Opposition from local communities, coupled with environmental concerns and stringent regulations, present some challenges. Despite these obstacles, the government appears committed to fostering growth in the sector and is actively working to attract more foreign investment.
The Warintza Project and Solaris Resources
One project that stands to gain from the Noboa administration is the Warintza Project, owned by Solaris Resources (TSX:SLS) (OTCQB:SLSSF). The company has signed an Investment Protection Agreement with the Ecuadorian Government, establishing a stable regulatory environment for the project. This includes assurances regarding mining regulations, security of title, and substantial new tax incentives aimed at accelerating development. The project provides a case for how a supportive administrative backdrop can aid individual initiatives in the mining sector.

Solaris Resources also recently made headlines for appointing China International Capital Corporation (CICC) as its financial advisor for its operations in China. CICC is a leading global investment bank, with its headquarters in Beijing and a strong foothold in the Chinese market, especially in matters related to mining sector transactions. The appointment follows multiple acquisition proposals Solaris has received for the Warintza Project, underlining the increasing interest in both the project and Ecuador’s mining sector more broadly.
Recent public commentary and analysts suggest that Daniel Noboa’s election is likely to have a positive influence on the mining industry in Ecuador. His commitment to a pro-business stance provides a favourable climate for both domestic and foreign investment. While challenges still exist, particularly concerning environmental regulations and community opposition, the path ahead looks promising for projects like Warintza. Ultimately, a Noboa administration could make Ecuador an increasingly attractive option for foreign investors, potentially opening the door for more significant international partnerships and investments.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The copper industry is facing challenges ranging from global shortages to price volatility. Copper’s role as a barometer for the global economy is due to the fact that it is required in everything from electrical equipment to industrial machinery. However, this widespread use has contributed to a shortage that shows no signs of abating until at least 2030. Demand continues to climb, outstripping a supply that is already stretched thin, and this has implications for a host of industries reliant on copper.
One of the immediate challenges facing the industry is the short-term volatility of copper prices. Copper prices began the year on a strong note, boosted by a weakening dollar and a surge in demand from a reopening Chinese economy. But alongside this demand, supply issues have also cropped up. Peru, accounting for 10% of the world’s copper supply, has been mired in protests, affecting its mining capabilities. While these short-term challenges have immediate repercussions, analysts are pointing towards a more seismic shift—a generational change in copper prices. This shift is concerning as mining companies, which have enjoyed an upswing in valuations due to the price rise, might find these gains unsustainable in the long term.
With supply unable to meet demand, alternatives are desperately needed. Higher prices could incentivize companies to explore new mining projects, extract from lower-grade resources, and even adopt new technologies to extend the lives of their existing projects. Recycling could also offer some relief, becoming a more appealing option as copper becomes pricier. Some end-users may also resort to using other metals like aluminum to replace copper, or they may seek ways to use less copper in their operations. While these alternatives might offer short-term solutions, they won’t solve it.
The undeniable reality is that many existing copper mines are running out of ore. Investments into new mines have been sluggish, lacking the billions of dollars needed to address the growing deficit. A new copper mine takes around 10 years to become operational, and decisions made today will have repercussions a decade down the line. This long lead time makes the capital commitment even more urgent, yet the industry is still lagging in this regard. The last major investment cycle was in the 1970s, and while there has been a recent uptick in exploration spending, the new discoveries are rare and insufficient to compensate for the decline in ore grades from older, larger mines. Global mined copper production is projected to decline sharply, creating a 15Mt supply shortfall by 2034. By that time, over 200 copper mines are expected to run out of ore. Although there are possible projects in the pipeline, it’s uncertain how many will actually become operational.
Ultimately, a long-term copper shortage still appears inevitable. Supported by growing demand, especially from the electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors, and compounded by supply chain disruptions and dwindling Latin American supplies, this shortage will likely become a defining issue for the industry. Major global commodity miners are investing in new projects, signalling a bullish outlook, but the shortfall is a looming problem that demands immediate action.
Tackling these challenges will require not just higher investments and quicker decision-making but also an industry-wide recognition of the severe supply-demand imbalance. Some solutions may be beginning to appear in the form of new projects and increased interest from investors. One example is Solaris Resources’ (TSX:SLS) Warintza Project in Ecuador. Solaris Resources recently announced the appointment of China International Capital Corporation (CICC) as its financial advisor for Chinese operations. CICC is a Beijing-based global investment bank with a strong foothold in the Chinese mining sector, particularly in mergers and acquisitions. This appointment comes in the wake of multiple acquisition proposals Solaris Resources has received for the Warintza Project.
Mr. Richard Warke, Executive Chairman, commented in a press release: “Warintza is a very special asset that has the potential to create tremendous long-term value for all stakeholders by unlocking one of the last major greenfield districts at low elevation and adjacent to infrastructure in the global copper industry. The Company has a rich opportunity to significantly grow the Project while advancing it through technical studies and permitting with financing consistent with my commitment to minimize shareholder dilution.”
The Warintza Project drawing attention and the appointment of CICC as the financial advisor are part of some broader trends across the copper mining industry. Chinese investors are increasingly looking at Ecuador’s mining sector with growing interest. Companies engaged in exploration projects in the region are fielding more calls and inquiries about potential collaborations or acquisitions. This uptick in interest can be seen as a reflection of the growing recognition that more copper projects are needed to address the looming global shortage and a path forward for miners.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

ATEX Resources (TSXV:ATX) has initiated its Phase IV drilling program at the Valeriano Project in Chile’s Atacama Region. The first three holes of this phase aim to explore and define the Central and Western High-Grade trends within the project area.
Raymond Jannas, President, and CEO of ATEX, commented in a press release: “We are incredibly excited to be commencing our Phase IV drill program during what continues to be a transformative year for ATEX and the Valeriano Project. To date, we have completed the successful Phase III drill program, delivering multiple intersections of over a thousand metres of continuous mineralization above 0.4% copper, leading to the announcement of a significant 1.41 billion tonne1 Inferred Mineral Resource Estimate in September. Following on from this, we then announced the results of a PEA-level metallurgical program demonstrating exceptional metal recoveries for the project and exceeding the recovery assumptions contemplated in the resource. Phase IV drilling is poised to build on this success and continue to further demonstrate the quality of the Valeriano Project.”
The initial hole to be completed, a continuation of ATXD-24, was paused at the conclusion of Phase III due to inclement weather conditions. Drilling is expected to resume for an additional 400 meters, focusing on an unexplored elevation of the Central Trend. This hole was previously stopped while in a high-grade Early Porphyry (EP) zone.
The second hole, which is a daughter hole stemming from VAL-12, begins at a depth of 605 meters and aims westward. This hole is intended to explore the Western Trend’s limits as well as the mineralization in rock-milled breccia to the west of the EP contact, an area that has not been investigated before.
The third hole is set to start upon the arrival of a third drilling rig and will also be a daughter hole, originating from ATXD-17. Planned to commence at a depth of 850 meters, the hole will be drilled westward to test the upper areas of the Central Trend before continuing into the Western Trend.
The Valeriano Copper-Gold Project, which ATEX is exploring, lies within an emerging mineral belt informally known as the Link Belt. This belt connects the El Indio High-Sulphidation Belt to the south with the Maricunga Gold Porphyry Belt to the north and is host to several copper-gold porphyry deposits in varying stages of development. Some notable projects in this belt include Filo del Sol by Filo Mining, Josemaria by Lundin Mining, Los Helados by NGEX Minerals and JX Nippon, La Fortuna by Teck Resources and Newmont, and El Encierro by Antofagasta and Barrick Gold.
Highlights from the project are as follows:
- TWO RIGS CURRENTLY OPERATING – Rigs set up to utilize existing drill holes (Figure 1).
- ATXD-24 is being completed from where it was suspended at the end of Phase III having intersected 670 metres of 0.84% Copper Equivalent “CuEq” (0.60% Cu, 0.24 g/t Au & 101 ppm Mo) from 1,173 metres, including 312 metres of 1.00% CuEq (0.73% Cu, 0.30 g/t Au and 77 ppm Mo) from 1,530 metres (Company news release July 13, 2023) in the Central Trend and;
- A daughter hole, ATXD-12A, targeting the western trend, drilling out of historical hole VAL-12 which intersected 44.0 metres of 0.48 % CuEq (0.30% Cu, 0.16 g/t Au & 110 ppm Mo) from 1,012 metres (Table 1).
- THIRD RIG MOBILIZING – Initial hole to target southern extension of Western Trend with a daughter hole out of ATXD-17 (1,160 metres of 0.78% CuEq (0.53% Cu, 0.28 g/t Au and 70 ppm Mo) including 550 metres of 1.03% CuEq (0.69% Cu, 0.39 g/t Au and 70 ppm Mo) (Company news release June 13, 2022).
- PHASE IV TARGETING RECORD METERAGE SEASON AT VALERIANO – Full program considers 15,000 to 20,000 metres (Phase III – 12,513 metres) of diamond drilling with ability to expand the program subject to results.
- BUILDING OFF PHASE III SUCCESS – Phase IV objectives are to further define and extend the High-Grade Porphyry Trends intersected in Phase II and III while also exploring beyond the currently defined dimensions of the mineralized corridor measuring approximately 1.0 X 1.0 kilometers which remains open in all directions.
Table 1. Summary Results for Phase IV Follow Up
| Hole ID | Year Drilled | From | To | Interval | Cu % |
Au g/t |
Ag g/t |
Mo g/t |
CuEq In Situ1 |
CuEq % MRE2 | CuEq % Met Recoveries3 |
| VAL-12 | 2012 | 1,012.0 | 1,056.0 | 44.0 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 110 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.44 |
| ATXD-17 | 2022 | 802.0 | 1,962.0 | 1,160.0 | 0.53 | 0.28 | 1.10 | 70 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.77 |
| Inc. | 1,280.0 | 1,830.0 | 550.0 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 1.30 | 70 | 1.03 | 0.98 | 1.02 | |
| ATXD-24 | 2023 | 1,173.0 | 1,842.4 | 669.4 | 0.60 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 101 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| Inc. | 1,530.0 | 1,842.4 | 312.4 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 1.11 | 77 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
1CuEq reported in situ ) assuming 100% recovery for component metals see Company news June 13, 2022 for ATXD-17 & July 13 2023 for ATXD-24
2CuEq calculated using recoveries assumed in 2023 MRE (90% Cu, 70% Au, 80% Ag and 60% Mo) (US$3.15/lb Cu, US$1,800/oz Au, US$23/oz Ag and US$20/lb Mo) (See Company news Sept, 12 2023) using the following formula Copper Equivalent (CuEq) is calculated using the formula CuEq % = Cu % + (6481.488523 * Au g/t /10000) + (94.6503085864 * Ag g/t /10000) + (4.2328042328 * Mo g/t /10000)
3CuEq calculated using recoveries reported from metallurgical test work results reported in Company news Oct, 18 2023 (95% Cu, 94% Au, 89% Ag and 83% Mo) (US$3.15/lb Cu, US$1,800/oz Au, US$23/oz Ag and US$20/lb Mo) using the following formula (((Cu % * Cu US$/lb * 22.0462))+((Au Recovery / Cu Recovery * Au g/t)*(Au US$/oz / 31.1034768))+((Ag Recovery / Cu Recovery * Ag g/t)*(Ag US/oz / 31.1034768))+((Mo Recovery / Cu Recovery * Mo ppm / 10000) * Mo US$/lb / 22.0462))/(Cu US$/lb * 22.0462)
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The Autazes Potash Project was spotlighted as a strategically important mineral initiative for Brazil at two recent high-profile events: the Expo & Brazilian Mining Congress (Exposibram 2023) and the International Amazon and New Economies Conference. Both conferences took place in Belém, PA, from August 28th to September 1st. Adriano Espeschit, President of Potássio do Brasil, was responsible for presenting the project. Espeschit focused on the crucial role of potash, particularly in Brazilian agribusiness, which is responsible for almost 10% of global food production.
The company initiated its presence at Exposibram 2023 with an educational booth designed to give attendees a thorough understanding of the upcoming potash fertilizer project in Autazes, AM. The company also participated in the second edition of the Canadian Breakfast Meeting where it introduced the Autazes Potash Project to suppliers involved in the mining sector. The most notable moment for Potássio do Brasil at Exposibram was undoubtedly Espeschit’s participation in a panel discussion about public policies for strategic minerals in Brazil. There, he detailed the role of the Autazes Potash Project in global food security, highlighting its grounding in Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. According to Espeschit, Potássio do Brasil has the potential to supply up to 20% of potassium chloride to the Brazilian agribusiness sector, which is significant considering that Brazil currently imports 98% of its potassium chloride.
Adriano Espeschit commented: “Potássio do Brasil can contribute up to 20% of potassium chloride supply to Brazilian agribusiness. Consumption that, in agribusiness, we are totally dependent on because we import 98%”. Our project is entirely sustainable. We will produce green potash with 80% less carbon footprint compared to projects in Canada and Russia, thanks to our Brazilian energy matrix, which is 84% renewable. By producing potash fertilizer, we are firmly committed to contributing to achieving the UN’s second Sustainable Development Goal, Zero Hunger.
Following Exposibram, representatives from Potássio do Brasil attended the International Amazon and New Economies Conference, which focused on a variety of topics including new economies, the bioeconomy, and circular economy. Over 130 companies and institutions in the mineral sector, including Potássio do Brasil, pledged to develop environmentally responsible practices to conserve the Amazon. Espeschit stated that the company’s participation and sponsorship of this event was an explicit commitment to sustainable development in the Amazon and bolstering food security globally, without causing environmental or social harm.
Notable speakers at the conference included global figures like South Korean diplomat Ban Ki-moon, former Prime Minister of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Tony Blair, and former President of Colombia Iván Duque Márquez. All emphasized the necessity of sustainable development as a means to reduce poverty. Márquez specifically invited the audience to ponder the future of new economies in the Amazon, stressing the importance of incorporating traditionally Amazon-related activities into development plans.
For context, the Expo & Brazilian Mining Congress is an annual event organized by the Brazilian Mining Institute (Ibram) and is one of Latin America’s most significant gatherings in the mineral sector. The event provides a robust platform for discussions about the mineral industry’s key scenarios and trends. The International Amazon and New Economies Conference, also coordinated by Ibram, brings together stakeholders from various sectors, including indigenous communities, academia, and both the public and private sectors, to discuss sustainable development and environmental issues. The conference aims to foster solutions that balance economic growth, inequality reduction, and conservation efforts.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The Australian government has announced it will double the funds allocated for its Critical Minerals Facility, increasing it to A$2 billion ($1.3 billion). The move aims to attract mining and processing companies, particularly those based in the United States, to establish operations in Australia.
Strategic Shift Amid Global Energy Transition
The decision to boost investment in critical minerals comes as Australia faces an anticipated decline in revenue from fossil fuel exports due to global decarbonization efforts. Government data shows that Australia’s lithium exports were valued at A$20 billion ($12 billion) for the year ending in June. According to government forecasts, earnings from this sector could soon be on par with that of thermal coal exports by 2028.
International Collaboration and the Critical Minerals Task Force
Talks have also been underway with American authorities regarding the establishment of a critical minerals task force. This would aim to boost private investment in Australia’s rare earths industry, while also reducing the world’s reliance on China for these crucial materials. Anthony Albanese, Prime Minister of Australia, will visit China—Australia’s largest trade partner—on November 4 to discuss various trade aspects, including those concerning critical minerals.
Australia’s Rich Mineral Reserves
According to a 2022 report by Geoscience Australia, the country ranks among the world’s top three in terms of recoverable resources for a range of critical minerals including bauxite, cobalt, copper, lithium, manganese, nickel, tungsten, vanadium, and zinc. Interestingly, 80% of Australia is still considered “under-explored,” offering ample opportunities for new mineral discoveries.
The increasing importance of critical minerals like lithium, copper, cobalt, and nickel in the global economy is affecting investment strategies for mining companies. As the transition to greener technologies accelerates, the demand for these minerals is expected to rise, thereby encouraging investment in mining and processing projects. This may also influence the balance of economic power among nations rich in these resources.
Australia holds a leading role in the production of these vital resources. It is the world’s largest lithium exporter, contributing to 53% of global production in 2022. It also ranks as the largest producer of zircon, bauxite, iron ore, and rutile and the fourth-largest producer of rare earths. The country is also the second-largest producer of cobalt, possessing around 19% of the world’s cobalt resources.
Frameworks and Initiatives for Investment
The government has implemented several programs to encourage international investment in Australia’s resource and energy sectors. The government has earmarked up to A$1 billion from the A$15 billion National Reconstruction Fund for value-adding resources. This could include investments into innovative technologies like exploration or drilling technologies. An additional A$3 billion has been allocated for renewable and low-emission technologies.
In a concerted effort to foster growth and international collaboration, the Australian government is increasing its investment in the critical minerals sector to record levels. This move aligns with global trends as countries pivot towards greener technologies, highlighting the importance of minerals like lithium, copper, and cobalt.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Arizona Metals (TSX:AMC) has reported new drilling data from its Kay Deposit in Arizona. The information derived from three additional drill holes reveals both the continuity of the mineral deposit and its potential for further expansion, especially toward the surface. Two of these new holes, labelled 116 and 114, were specifically aimed at gauging the deposit’s upward extension using a modified drilling rig. The drill holes managed to extend the mineralization by 65 meters and 55 meters upward, substantially enlarging the area of the deposit above previously drilled levels.
Marc Pais, CEO of Arizona Metals, commented in a press release: “These new drill results from the Kay Deposit continue to point to its expansion potential, in this case adding 65 m to the drilled vertical extent of the deposit, which has now been drilled over more than 900 m vertically. Our specially modified drill rig will continue to test these shallower portions of the deposit along the more than 350 m of strike length defined to date, while we also expand mineralization with the second rig targeting northern and southern extensions of the Kay Deposit.”
Looking ahead, Arizona Metals Corp. has outlined its immediate focus on the Western Target within the same property. The company will complete and submit an exploration plan of operations (EPO), a procedural step that will enable further infrastructure development like road and drill pad construction. This is aimed at testing several high-priority targets both at the Western Target and across the broader property. Concurrently, a property-wide sampling program of roughly 1,900 samples is underway, the assay results of which will be instrumental in refining the upcoming EPO and identifying other areas of high mineral value.
The company operates two drill rigs at the Kay Deposit, with a specific focus on both infill and expansion drilling. The estimated drilling is around 30,000 meters, targeted toward the zones outlined in their recent findings. The company aims to provide a comprehensive maiden mineral resource estimate (MRE) in due course. While the exact amount of required drilling for the MRE remains to be determined, the company will offer updates on the timing as the drilling continues throughout 2024.
As for the overall progress and financial standing of Arizona Metals Corp., the company has, to date, completed 93,000 meters of drilling on the Kay Exploration Project. Armed with a cash reserve of $43 million as of the end of June 2023, the company can finish the remaining 66,000 meters in its third-phase drilling program, which has a budget allocation of $27.7 million.

Highlights from the results are as follows:
- Hole KM-23-115 intersected 83.7 m at 3.6 g/t gold equivalent (AuEq), including 15.3 m at 6.3 g/t AuEq. This hole is in the core of the deposit, infilling a 50-m gap between holes KM-21-41 and KM-23-105, and demonstrating excellent continuity of grade and thickness in this region of the deposit (Figures 1 and 2).
- Hole KM-23-116 returned three separate mineralized intervals, including 21.9 m at 1.3% CuEq, which includes 1.4 m at 5.7% CuEq.
- Hole KM-23-114 intersected five separate mineralized intervals, including 22.1 m at 0.6% CuEq and 3.7 m at 1.2% CuEq.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Titan Mining (TSX:TI) has announced the discovery of the Kilbourne graphite trend, situated on the lands where the Empire State Mine is currently operational in upstate New York. Preliminary assessments indicate that the Kilbourne target could potentially contain between 3.36 million tons and 26.25 million tons of graphite, grading 2.0% to 4.5%. However, these estimates are based on available drill data and are still conceptual, lacking enough exploration to define a current mineral resource. The company has emphasized that further exploration may not necessarily result in a confirmed mineral resource.
Donald Taylor, President and CEO of Titan Mining, commented in a press release: “Natural flake graphite is a critical material in the production of lithium-ion batteries with significant and increasing demand. The confirmation of a global scale flake graphite target on the Company’s land package is an especially significant development in the history of the Company.”
The Kilbourne target emerged from an analysis of historic geological data and recent drilling activities. The host rocks’ high metamorphic grade has increased the size and characteristics of the contained graphite to flake sizes. To date, 53 drill holes have been tested for the presence of graphite, all of which showed graphite content. However, only six of these have been assayed for graphite quality. The company has engaged an independent laboratory to conduct further testing and evaluation.
Graphite’s presence in this particular district is not new and has historical precedents dating back to the first half of the 20th century. Titan Mining currently holds over 80,000 acres of mineral rights in St. Lawrence County, NY and plans to continue evaluating data for additional graphite exploration targets.
Graphite is a naturally occurring form of pure carbon and is critical for a range of industrial and energy applications, including lithium-ion batteries. The United States currently lacks domestic sources for natural flake graphite, a situation that has raised concerns given the rising demand for this resource. The U.S. Department of Energy anticipates that by 2025, the demand for graphite will outstrip production by 79%. This gap is expected to widen substantially by 2035.
Currently, China dominates the global graphite supply, providing more than 60% of the world’s graphite. The scarcity of domestic resources has landed graphite on the U.S. Department of Energy’s critical materials list, especially in light of the burgeoning electric vehicle and battery manufacturing sectors in the United States. Given the environmental and financial costs of synthetic graphite, natural graphite is increasingly seen as a viable alternative, particularly as concerns about the sourcing of critical materials continue to grow.

At present, the United States has only two graphite deposits that have reached the pre-feasibility stage or beyond: the Graphite Creek Deposit in Alaska and the Coosa Graphite Project in Alabama.
Highlights from the results are as follows:
- At or near surface targets with geological potential totaling between 210 and 1,050 million tons (Mt) grading between 2.0% and 4.5% graphitic carbon (Cg)
- Flake graphite is a key input to the auto industry battery supply chain and designated as a Critical Material by the United States Department of Energy
- There is no domestic source of flake graphite production; China, which accounts for more than half of global production, has recently announced export restrictions that may threaten the market
- ESM lands hosting the Kilbourne graphite trend are fully permitted for drilling with some portions of these lands also currently permitted for mining
- Aggressive plan to fast-track exploration and development with goal of being first domestic supplier of materials to the auto industry battery market
Table 1: Kilbourne Drilling Intercepts
| 2020-2022 Kilbourne Drilling | |||||||
| Hole ID | From (ft) | To (ft) | Interval (ft) | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Cg% |
| SX20-2563 | 632.3 | 665.6 | 33.3 | 192.7 | 202.9 | 10.1 | 3.1 |
| 673.9 | 697.0 | 23.1 | 205.4 | 212.4 | 7.0 | 1.5 | |
| 723.1 | 760.8 | 37.7 | 220.4 | 231.9 | 11.5 | 2.3 | |
| SX20-2564 | 652.0 | 742.5 | 90.5 | 198.7 | 226.3 | 27.6 | 2.3 |
| SX20-2565 | 612.0 | 642.0 | 30.0 | 186.5 | 195.7 | 9.1 | 3.1 |
| 742.0 | 768.1 | 26.1 | 226.2 | 234.1 | 8.0 | 1.9 | |
| SX21-2589 | 0.0 | 47.9 | 47.9 | 0.0 | 14.6 | 14.6 | 3.3 |
| SX21-2601 | 70.0 | 101.2 | 31.2 | 21.3 | 30.8 | 9.5 | 2.1 |
| SX22-2621 | 1,031.9 | 1,140.0 | 108.1 | 314.5 | 347.5 | 32.9 | 2.6 |
| 1,243.9 | 1,255.0 | 11.1 | 379.1 | 382.5 | 3.4 | 1.9 | |
| 1,310.0 | 1,350.0 | 40.0 | 399.3 | 411.5 | 12.2 | 3.1 | |
| 1,375.0 | 1,400.0 | 25.0 | 419.1 | 426.7 | 7.6 | 2.1 | |
| 1,465.0 | 1,831.0 | 366.0 | 446.5 | 558.1 | 111.6 | 2.2 | |
| Including | 1,495.0 | 1,510.0 | 15.0 | 455.7 | 460.2 | 4.6 | 3.3 |
| and | 1,530.0 | 1,560.0 | 30.0 | 466.3 | 475.5 | 9.1 | 3.5 |
| and | 1,695.0 | 1,831.0 | 136.0 | 516.6 | 558.1 | 41.5 | 3.1 |
Table 2: Kilbourne Collar Information (NAD 1983 UTM Zone 18N)
| Collars | ||||||
| Hole ID | Length (ft) | Easting (m) | Northing (m) | Elevation (m) | Azimuth | Dip |
| SX20-2563 | 3153 | 465846 | 4902302 | 186.010 | 120 | -55 |
| SX20-2564 | 3487 | 465846 | 4902302 | 186.010 | 125 | -63 |
| SX20-2565 | 3407 | 465846 | 4902302 | 186.100 | 125 | -50 |
| SX21-2589 | 2287 | 467176 | 4902744 | 186.000 | 0 | -90 |
| SX21-2601 | 1877 | 466948 | 4902442 | 193.000 | 0 | -90 |
| SX22-2621 | 3487 | 469184 | 4903668 | 182.837 | 150 | -70 |
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Puma Exploration (TSXV:PUMA) has reported findings from the first 11 holes of its 2023 drilling program at its Williams Brook Gold Project in Northern New Brunswick. The company reported that seven of these 11 holes returned significant amounts of gold, with four holes intersecting multiple high-grade gold quartz veins. Notably, Hole WB23-125 intersected 15 separate quartz veins and showed significant levels of gold, including an interval that measured 6.46 grams per ton (g/t) of gold at a depth of 75 meters.
Puma Exploration President and CEO Marcel Robillard commented in a press release: “The first holes of our Phase 1 2023 campaign were drilled to map and test the newly identified veins discovered at surface at Lynx earlier this year and the depth continuity of the interpreted high-grade shoots at Lynx. Many holes hit multiple quartz veins downhole, often starting at surface. Hole 125 was drilled to 170 m depth, and we saw VG in 4 veins from 55 to 79 m depth. Those returned grades of 11.20 to 42.60 g/t gold over 0.35 to 0.80 m width. What’s most impressive is we intersected 15 veins, and they all contributed gold, regardless of whether they contained VG. That’s significant because it highlights the continuity of mineralization at Lynx and the potential for a large mineable system that remains open along strike and depth. Assay results for the remaining holes drilled deeper that returned numerous VG specks should be in soon. We expect they will extend the width and depth of the gold chutes and continue to build volume at Lynx.”
The 11 holes were initially reported on August 2, 2023, and were not part of the drilling series that yielded over 100 visible specks of gold upon first inspection. Assay results from these 11 holes ranged from anomalous gold levels of 0.1 g/t to as high as 42.60 g/t. These results support the indication of considerable continuity and depth extension of gold mineralization in the Lynx Gold Zone.
The drilling also explored previously untested areas and found broad mineralized zones, indicating the existence of additional gold chutes. For instance, results included 0.5 meters of 16.1 g/t gold in WB23-128 and 19.35 meters of 0.54 g/t gold in WB23-131. Results for the remaining 13 holes in the 2023 drilling program are still pending and will be made public upon receipt.
The Phase 1 drilling effort was primarily concentrated on the Lynx and Moose areas and aimed to confirm and extend high-grade gold mineralization. The program expanded from 15 to 24 holes after successfully intercepting depth extensions of high-grade shoots previously defined by other drilling initiatives.
In a geological context, most of the drilled holes showed widespread sericitization. However, visible gold and potential bonanza-grade veins were found to be associated with carbonate alteration, specifically dolomite, as well as with sulphide assemblages of pyrite, chalcopyrite, galena, and sphalerite occurring either as disseminated massive sulphides or semi-massive veinlets within the quartz veins.

Highlights from the results are as follows:
- Hole WB23-125 returned 50.85 m of 1.05 g/t gold.
- Gold mineralization extends over 90 m from surface in a series of stacked high-grade quartz veins.
- All 11 holes intersected the targeted quartz veins, with assay results returning from anomalous gold (0.10 g/t) to 42.60 g/t.
- Gold was intercepted at depth in areas never drilled before.
- Results confirm the continuity of gold mineralization at the Lynx Gold Zone.
- Assay results for 13 additional holes (2,200 m), including 47 samples containing VG are still pending
Table 1. Assay results of 2023 drilling
| DDH # | From (m) | To (m) | Length (m) | Au (g/t) |
| WB23-123 | 7.60 | 8.00 | 0.40 | 1.03 |
| WB23-125 | 2.90 | 93.55 | 90.65 | 0.70 |
| Incl. | 42.05 | 92.90 | 50.85 | 1.05 |
| Incl. | 66.25 | 92.90 | 26.65 | 1.70 |
| Incl. | 75.40 | 92.90 | 17.50 | 2.32 |
| Incl. | 78.65 | 92.90 | 14.25 | 2.67 |
| and | 75.40 | 79.90 | 4.50 | 6.46 |
| Individual samples | ||||
| 2.90 | 3.95 | 1.05 | 4.60 | |
| 11.00 | 11.30 | 0.30 | 9.87 | |
| 37.30 | 37.60 | 0.30 | 4.30 | |
| 42.05 | 42.40 | 0.35 | 2.85 | |
| 55.50 | 55.90 | 0.40 | 16.60 | |
| 66.25 | 66.60 | 0.35 | 13.30 | |
| 75.40 | 75.80 | 0.40 | 4.45 | |
| 76.05 | 76.25 | 0.20 | 1.71 | |
| 78.65 | 79.50 | 0.85 | 11.20 | |
| 79.50 | 79.90 | 0.40 | 42.60 | |
| 87.15 | 87.45 | 0.30 | 3.67 | |
| 88.00 | 88.40 | 0.40 | 11.05 | |
| 90.45 | 90.80 | 0.35 | 2.44 | |
| 91.75 | 92.35 | 0.60 | 5.32 | |
| 92.35 | 92.90 | 0.55 | 1.46 | |
| WB23-127 | 85.90 | 86.40 | 0.50 | 1.50 |
| WB23-128 | 95.15 | 95.65 | 0.50 | 16.10 |
| WB23-129 | 42.90 | 53.00 | 10.10 | 3.30 |
| Incl. | 45.25 | 48.45 | 3.20 | 10.36 |
| Incl. | 48.07 | 48.42 | 0.35 | 29.20 |
| WB23-131 | 46.25 | 65.60 | 19.35 | 0.54 |
| Incl. | 47.00 | 48.05 | 1.05 | 1.06 |
| and | 53.80 | 59.75 | 5.95 | 1.39 |
| Incl. | 57.60 | 58.10 | 0.50 | 12.35 |
| WB23-132 | 85.50 | 89.65 | 4.15 | 3.18 |
| Incl. | 86.15 | 89.07 | 2.92 | 4.43 |
| Incl. | 86.15 | 86.70 | 0.55 | 15.70 |
| and | 87.64 | 88.56 | 0.92 | 4.04 |
*Interval widths reported; true widths of the system are not yet known.
Table 2. Coordinates of drill holes
| DDH # | Easting (m)* |
Northing (m)* |
Elevation (m) |
Azimuth (°) |
Dip (°) |
Length (m) |
| WB23-122 | 660246 | 5259235 | 386 | 335 | -45 | 107.0 |
| WB23-123 | 660256 | 5259214 | 386 | 335 | -65 | 83.0 |
| WB23-124 | 660213 | 5259379 | 392 | 155 | -80 | 122.0 |
| WB23-125 | 660263 | 5259293 | 386 | 330 | -45 | 170.0 |
| WB23-126 | 660242 | 5259412 | 389 | 155 | -65 | 80.0 |
| WB23-127 | 660237 | 5259421 | 389 | 155 | -75 | 134.0 |
| WB23-128 | 660236 | 5259382 | 389 | 155 | -85 | 116.0 |
| WB23-129 | 660263 | 5259417 | 389 | 155 | -65 | 65.0 |
| WB23-130 | 660207 | 5259347 | 388 | 155 | -80 | 113.2 |
| WB23-131 | 660227 | 5259340 | 389 | 165 | -65 | 89.0 |
| WB23-132 | 660303 | 5259443 | 388 | 230 | -45 | 196.0 |
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

In a major acquisition that is expected to reshape Chile’s role in the lithium industry, the country’s state-owned copper mining company, Codelco, has entered into an agreement to acquire Lithium Power International (LPI) for A$385 million, approximately US$244 million. The acquisition is a first of its kind for Codelco and marks a major step for the company within the lithium sector, as outlined by the Chilean government’s public-private model announced earlier this year.
The agreed-upon deal, which comes after weeks of negotiations, includes a cash offer of $0.57 Australian dollars per LPI share. A shareholder vote in January 2024 is required for the transaction to proceed. Lithium Power, which is an Australian company, has significant assets in Chile, most notably its Maricunga project. Located within the ‘Lithium Triangle’ in northern Chile, this flagship project is estimated to hold around 1.9 million tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE).
Prior to this deal, Lithium Power had divested its assets in Western Australia back in June, to concentrate on the Maricunga project. The Maricunga asset is considered a strong and cost-effective operation. According to a Definitive Feasibility Study completed by WorleyParsons and released in the first quarter of 2022, the project has an operating expense of $3,718 per tonne and supports an annual production of 15,200 tonnes of LCE over a 20-year mine life. The same study also placed the project’s net present value at $1.98 billion before tax. Notably, the project has received environmental approval from Chilean authorities as of February 2020.
Codelco Chairman Maximo Pacheco stated that the acquisition exemplifies how the company intends to become “a globally relevant supplier of critical metals to enable the energy transition.” Despite this, some industry analysts have questioned Codelco’s ability to navigate the lithium market, given that it has traditionally operated as a copper miner and has no prior experience in lithium extraction.
Codelco has also recently faced some financial challenges, posting its lowest production in nearly 25 years. The company’s output has decreased by 17% and is projected to continue falling until 2025. Earlier this month, Moody’s Investors Service also downgraded Codelco’s investment-grade credit rating.
The Chilean government’s new public-private partnership model for the lithium sector, unveiled in April, has assigned a key position to Codelco. The model calls for such partnerships for future lithium projects in an attempt to further solidify Chile’s standing in the global lithium market. Currently, Chile is the world’s second-largest producer of lithium, trailing only Australia, and possesses the largest known lithium deposits globally.
Lithium Power International is a pure-play lithium company with three distinct project regions: one in South America’s brine region and two in Western Australia. The company’s main focus has been on the development of Chile’s next sustainable high-grade lithium mine, supported by a robust infrastructure that includes accommodations, labs, workshops, and a range of utilities and supplies, among other facilities.
As the transaction awaits shareholder approval, the acquisition will be watched closely, particularly concerning Chile’s ambitions to become a dominant force in the lithium industry, which is critical for batteries in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Kodiak Copper (TSXV:KDK) has released results from its drill program at the MPD copper-gold porphyry project, which it owns entirely, in southern British Columbia. The company applied an exploration model similar to Cadia-Ridgeway or Red Chris, leading to the discovery of a larger porphyry system in the project’s West Zone. The model helped identify mineralized zones near high-angle structural controls and changes in geology. This technique has also proven effective in discovering high-grade zones at the nearby Copper Mountain mine earlier this year.
Chris Taylor, Chairman of Kodiak, commented in a press release: “The West Zone is clearly significantly larger than past explorers had appreciated and contains higher grades as well, where copper and gold are concentrated by key geological features. The significant near-surface copper at the West Zone and other porphyry centres at MPD are an attractive complement to the deeper higher-grade mineralization discovered by Kodiak at the Gate Zone.”
Three drill holes, designated as AXE-23-005, 006, and 007, aimed to explore the northern extents of the West Zone but faced difficult drilling conditions and did not reach their target depths. Two additional holes, AXE-23-008 and AXE-23-011, drilled from separate pads in the south-central part of the West Zone, extended the width and strike of mineralization and confirmed a new zone down to a depth of 962 meters.
Recent efforts have led to the deepest copper-gold porphyry intercepts ever reported from the MPD project, highlighting that the mineralization there is more extensive and intricate than previously understood.
The MPD project covers 226 square kilometers and is strategically located near several operating mines in southern Quesnel Terrane, a primary copper-gold production area in British Columbia. The site is easily accessible year-round and is situated between the towns of Merritt and Princeton, benefiting from good infrastructure in the vicinity.


Highlights from the results are as follows:
- Best ever drill holes at the West Zone, following the application of a Cadia-Ridgeway or Red Chris “style” of exploration model that targets higher grades and significant vertical extents within the total mineralized system.
- Shallow high-grade copper assaying 1.17% Cu (1.26% CuEq*) over 39 metres, within 0.33% Cu (0.39% CuEq*) over 198 metres, starting at 33 metres depth in drill hole AXE-23-008.
- Best mineralized interval reported from the West Zone to date; 0.49% Cu (0.58% CuEq*) over 254 metres, within 0.21% Cu (0.27% CuEq*) over 941 metres starting at bedrock surface in drill hole AXE-23-011.
- Holes AXE-23-008 and 011 confirmed the high-energy, mineralized hydrothermal breccia at depth in the West Zone, as first reported in AXE-23-002 (news release July 27, 2023). This new zone has now been extended to 185 metres of strike and remains open in all directions.
- New and historic drilling at the West Zone has confirmed porphyry mineralization over an area of 300 metres by 650 metres, and from surface to depths of 962 metres, which is open to extension.
- Hole AXE-23-011, drilled vertically in the southern portion of the West Zone, intersected mineralization from bedrock surface to 962 metres depth, assaying 0.49% Cu, 0.29 g/t Au and 1.30 g/t Ag (0.58% CuEq*) over 254 metres, within 0.21% Cu, 0.16 g/t Au and 0.64 g/t Ag (0.27% CuEq*) over an impressive intercept of 941 metres.
- Hole AXE-23-011 also added 185 metres of strike to the new mineralized hydrothermal breccia zone, assaying 0.32% Cu, 0.16 g/t Au and 0.95 g/t Ag (0.37% CuEq*) over 89 metres from 873 to 962 metres. Figure 4
- Hole AXE-23-008, drilled north along strike, intersected mineralization from near surface to 540 metres depth, assaying 0.33% Cu, 0.18 g/t Au and 0.88 g/t Ag (0.39% CuEq*) over 198 metres, within a broader zone of 0.18% Cu, 0.16 g/t Au and 0.59 g/t Ag (0.25% CuEq*) over 519 metres.
- Hole AXE-23-008 also encountered the new hydrothermal breccia zone over 153 metres from 735 to 888 metres, assaying 0.11% Cu, 0.17 g/t Au and 0.52 g/t Ag (0.19% CuEq*). Figure 4
- Hole AXE-23-007 extended the northern boundary of the West Zone mineralized envelope with 0.10% Cu, 0.11 g/t Au and 0.36 g/t Ag (0.15% CuEq*) over 182 metres.
- Two additional holes, AXE-23-005 and 006, were abandoned before reaching target depths due to difficult ground conditions. These holes nonetheless intersected moderate to high-grade gold in vein-like structures that enrich the porphyry mineralization, including 0.04% Cu and 4.54 g/t Au over 6 metres from 48 metres depth in drill hole AXE-23-005, and 0.12% Cu and 2.08 g/t Au over 4 metres from 71 metres depth in drill hole AXE-23-006
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Arizona Sonoran Copper (TSX:ASCU) has reported its latest Mineral Resource Update (MRE) for its Cactus Project, a combined initiative that includes the Cactus, Stockpile, and Parks/Salyer deposits. Situated 45 miles south of Phoenix, Arizona, the Cactus Project is expected to be the focus of an upcoming Pre-Feasibility Study slated for release in the first quarter of 2024. The goal is to establish a copper cathode heap leach and SXEW operation that produces 45-50 thousand tons per annum (ktpa).
The Cactus Project is an entirely-owned brownfield project located on private land in Arizona. The site comes with approximately $30 million worth of existing infrastructure, an advanced stage of permitting, approved water rights, and ready access to water sources.
George Ogilvie, CEO of Arizona Sonoran Copper Company commented in a press release: “Our team has completed yet another key milestone in the process of reactivating the Cactus Mine. Driven through textbook infill drilling programs at Parks/Salyer and Cactus, our team readies an already significant copper asset in Arizona, USA for the next step in technical reporting; 3.6 billion pounds of Copper were added and converted to the M&I category for a new M&I mineral resource of 5.2 billion pounds. The leachable Copper M&I category now stands at 4.4 billion pounds of Copper and will act as the foundation for our upcoming PFS. The PFS remains on track and on budget for Q1 2024. I look forward to our team continuing to deliver on key objectives over the next year.”
The newly updated MRE is backed by extensive drilling programs concentrated on the northeastern portion of the Santa Cruz porphyry copper system, to which the company has access to around 3.5 miles. The drilling data has been categorized into Measured, Indicated, and Inferred resources based on the spacing between drilling points. Specifically, a total of 80,715 feet of new drilling into the Cactus deposits has been carried out since May 2021, and new Parks/Salyer drilling accumulated to 57,250 feet from July 2022 to March 2023. The company plans to continue drilling beyond April 2023 with the intention of releasing another mineral resource update in 2024.
In terms of geology, the resource areas within the Cactus Project consist of fragmented parts of the larger Santa Cruz Porphyry System. The mineral deposits are hosted mainly in Precambrian Oracle granite and Laramide monzonite porphyry. The geology of the site is complex, with notable fracturing, faulting, and both pre-mineral and post-mineral brecciation. The resource areas also contain both oxide and enriched copper mineralization, lying above the primary sulphide mineralization. This geological complexity and the continuity of mineralization styles suggest that the resource areas might have once been interconnected, which assists in further exploration and modelling of the resources.

Cactus Project Resource Modelling
The resource modelling for the Cactus Project was carried out by Arizona Sonoran Copper Company Inc.’s (ASCU) resource team and Allan Schappert, a qualified individual as per the National Instrument 43-101 standards for mineral projects. The team utilized updated drilling data and interpretations to form the basis of the Mineral Resource model, which was developed in Vulcan software.
The data used for generating the mineral resources included a significant number of drill holes and measurements. Specifically, the Cactus Project involved 305 drill holes totalling 309,418.5 feet; Parks/Salyer had 77 drill holes with 172,166.3 feet; and the stockpile had 518 drill holes totalling 44,728.2 feet. This drilling data is backed by standard quality assurance and control programs, and the quality of the data has been deemed suitable for use in resource estimation.
When it comes to the mineralized domains, these align with what one would expect for porphyry copper systems. These domains represent varying rock types and copper mineral zones, which in turn are associated with weathering processes that lead to secondary copper enrichment. Several mineral zones including leached, oxide, enriched, and primary were identified through logging and sequential copper analyses.
Physical density measurements were also an integral part of the resource modelling. Both historical data from ASARCO and recent measurements by ASCU were included. For the Cactus and Parks/Salyer deposits, density was measured using the wet and dry weight method with thousands of samples considered for accurate assessment. For the stockpile, given its unconsolidated nature, density was calculated based on weight and volume measurements from four test holes.
Copper grades were estimated using a technique called Ordinary Kriging. A range of statistical and visual validation methods were employed, ensuring the reliability of these estimates. This included comparisons of statistical distribution, visual cross-checks against the drilling data, and other methods like change of support and swath plots.
Updates on Parks/Salyer and Cactus Deposits


Parks/Salyer showed a notable increase in its leachable Indicated mineral resource, rising from 2,461 million pounds (Mlbs) in the 2022 Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA) to 2,677 Mlbs. This increase is attributed to successful infill drilling, the inclusion of mineral resources under a new Mineral Exploration Permit obtained in October 2024, and a slight natural extension of mineralization onto the MainSpring property.
In the case of the Cactus deposits, the focus of Measured and Indicated drilling programs was on upgrading the Inferred mineral resources from the PEA to support the upcoming Pre-Feasibility Study. The total leachable Measured and Indicated resources for Cactus were reported to be 156.3 million tons at a grade of 0.491% Cu TSol, distributed between open pit and underground mineral resources. The Cactus East sector notably contains 41.2 million tons at a much higher grade of 1.057% Cu TSol.
Stockpile Conversion and Classification
The Stockpile saw a significant shift from Inferred to Indicated classification. Previously categorized solely as Inferred, recent drilling efforts have converted 217 million pounds of copper at a grade of 0.153% Cu TSol into the Indicated category. Only 3 million pounds now remain in the Inferred category. This change does indicate a minor reduction in total pounds, but the grade increased, largely due to higher copper grades in the upper lift of the stockpile.
Highlights and results from the MRE are as follows:
| PREVIOUS MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of September 28, 2022) |
UPDATED MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2023) |
VARIANCE | |||||
| Tons | Grade | Pounds | Tons | Grade | Pounds | Cu Content | |
| kt | Cu%¹ | Cu Mlbs | kt | Cu%¹ | Cu Mlbs | % | |
| Total Measured |
N/A |
10,400 |
0.241 |
49.8 |
New |
||
| Leachable |
9,100 |
0.230¹ |
41.9 |
New |
|||
| Primary |
1,300 |
0.315 |
8.0 |
New |
|||
| Total Indicated |
151,800 |
0.531 |
1,610.7 |
435,300 |
0.589 |
5,124.2 |
+218% |
| Leachable |
73,900 |
0.723 |
1,065.2 |
348,500 |
0.629¹ |
4,387.2 |
+312% |
| Primary |
77,900 |
0.350 |
545.5 |
86,800 |
0.425 |
737.0 |
+35% |
| Total M&I |
151,800 |
0.531 |
1,610.7 |
445,700 |
0.580 |
5,174.0 |
+221% |
| Leachable |
73,900 |
0.723 |
1,065.2 |
357,600 |
0.619¹ |
4,429.0 |
+316% |
| Primary |
77,900 |
0.350 |
545.5 |
88,000 |
0.423 |
745.0 |
+37% |
| Total Inferred |
449,900 |
0.544 |
4,894.2 |
233,800 |
0.472 |
2,207.9 |
-55% |
| Leachable |
310,400 |
0.590 |
3,663.7 |
107,700 |
0.607¹ |
1,307.9 |
-64% |
| Primary |
139,500 |
0.441 |
1,230.5 |
126,200 |
0.357 |
900.0 |
-27% |
NOTES:
1. Leachable copper grades are reported using sequential assaying to calculate the soluble copper grade. Primary copper grades are reported as total copper, Total category grades reported as weighted average copper grades of soluble copper grades for leachable material and total copper grades for primary material. Tons are reported as short tons.
2. Stockpile resource estimates have an effective date of 1st March, 2022, Cactus resource estimates have an effective date of 29th April, 2022, Parks/Salyer resource estimates have an effective date of 19th May, 2023. All resources use a copper price of US$3.75/lb.
3. Technical and economic parameters defining resource pit shell: mining cost US$2.43/t; G&A US$0.55/t, 10% dilution, and 44°-46° pit slope angle.
4. Technical and economic parameters defining underground resource: mining cost US$27.62/t, G&A US$0.55/t, and 5% dilution,
5. Technical and economic parameters defining processing: Oxide heap leach (HL) processing cost of US$2.24/t assuming 86.3% recoveries, enriched HL processing cost of US$2.13/t assuming 90.5% recoveries, Primary mill processing cost of US$8.50/t assuming 92% recoveries. HL selling cost of US$0.27/lb; Mill selling cost of US$0.62/lb.
6. Royalties of 3.18% and 2.5% apply to the ASCU properties and stateland respectively. No royalties apply to the MainSpring (Parks/Salyer South) property.
7. For Cactus: Variable cutoff grades were reported depending on material type, potential mining method, and potential processing method. Oxide material within resource pit shell = 0.099% TSol; enriched material within resource pit shell = 0.092% TSol; primary material within resource pit shell = 0.226% CuT; oxide underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.549% TSol; enriched underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.522% TSol; primary underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.691% CuT.
8. For Parks/Salyer: Variable cut-off grades were reported depending on material type, associated potential processing method, and applicable royalties. For ASCU properties – Oxide underground material = 0.549% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.522% TSol; primary underground material = 0.691% CuT. For stateland property – Oxide underground material = 0.545% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.518% TSol; primary underground material = 0.686% CuT. For MainSpring (Parks/Salyer South) properties – Oxide underground material = 0.532% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.505% TSol; primary underground material = 0.669% CuT.
9. Mineral resources, which are not mineral reserves, do not have demonstrated economic viability. The estimate of mineral resources may be materially affected by environmental, permitting, legal, title, sociopolitical, marketing, or other relevant factors.
10. The quantity and grade of reported inferred mineral resources in this estimation are uncertain in nature and there is insufficient exploration to define these inferred mineral resources as an indicated or measured mineral resource; it is uncertain if further exploration will result in upgrading them to an indicated or measured classification.
11. Totals may not add up due to rounding.
- 221% increase of total Measured and Indicated (“M&I”) resources (including primary resources), and a 9% increase of grade, resulting in a 55% decrease of Inferred resources due to upgrading of material
- MRE including Primary Resource Opportunity
- M&I 445.7 Mt @ 0.58% Cu for 5.17 billion pounds of copper
- Inferred 233.8 Mt @ 0.47% Cu for 2.21 billion pounds of copper
- Leachable (Oxide and Enriched) Mineral Resource
- M&I category increases by 316%: 357.6 million tons (“Mt”) at 0.62% Soluble Copper (“Cu TSol”) for 4.43 billion lbs of copper
- Inferred Category decreases by 64%: 107.7 Mt at 0.61% Cu TSol for 1.31 billion lbs of copper due to upgrading of material
- Low discovery cost – $0.005 / lb per pound
- +1.0% Soluble Copper Grades – specifically, Parks/Salyer contains 130Mt @ 1.028% Cu Tsol and Cactus East contains 41.2Mt @ 1.057% Cu TSol within M&I resources reporting to underground resource cutoff grades.
- Continuity confirmed – total drill database includes 526,000 ft (160,420 m) of drilling in 900 holes, resulting in demonstrated consistency of mineralization overall and a significant upgrade of the Parks/Salyer Deposit from the last MRE
- High Quality – first declaration of Measured mineral resources and significant conversion of Inferred mineral resources to the Indicated category which have the potential to be used to declare first reserves in the pending Pre-Feasibility Study expected in Q1 2024
- Location Advantages – set within Casa Grande’s industrial park and connected to nationwide transportation (highway and railroad), a streamlined permitting process, access to Arizona Public Service power, and access to water
- Growth – ongoing drilling will focus on Parks/Salyer southern extensions (Parks/Salyer South property); exposure to a 4 km mine trend with pockets of mineralization known south of Parks/Sayler, in the Gap Zone and NE of Cactus East
- Next Steps – Continue decreasing drill spacings to 125 ft (38 m) for future studies; begin drilling at the MainSpring (Parks/Salyer South) property
TABLE 2: Parks/Salyer Deposit
| PREVIOUS MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of September 28, 2022) |
UPDATED MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2023) |
|||||
| Tons | Grade | Pounds | Tons | Grade | Pounds | |
| kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | |
| Total Indicated | N/A | 143,900 | 1.009 | 2,906.1 | ||
| Total Leachable | 130,200 | 1.028* | 2,676.6 | |||
| Oxide | 10,000 | 0.921* | 183.7 | |||
| Enriched | 120,200 | 1.037* | 2,493.0 | |||
| Total Inferred | 143,600 | 1.015 | 2,915.4 | 48,400 | 0.967 | 936.1 |
| Total Leachable | 115,400 | 1.066* | 2,460.9 | 44,500 | 0.982* | 873.2 |
| Oxide | 14,100 | 0.827* | 233.7 | 8,700 | 0.925* | 161.7 |
| Enriched | 101,200 | 1.100* | 2,227.2 | 35,700 | 0.996* | 711.5 |
NOTES: refer to TABLE 1
*Denotes Cu TSol, generated using a sequential assaying technique to calculate the grade of the soluble copper.
TABLE 3: Cactus East, Underground Resource outside of Cactus Open Pit Resource
| PREVIOUS MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of September 28, 2022) |
UPDATED MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2023) |
|||||
| Tons | Grade | Pounds | Tons | Grade | Pounds | |
| kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | |
| Total Indicated | 9,900 | 0.912 | 180.0 | 10,400 | 0.882 | 182.6 |
| Leachable | 7,700 | 0.954* | 146.2 | 9,000 | 0.891* | 161.0 |
| Total Inferred | 19,200 | 0.873 | 335.9 | 6,400 | 0.785 | 100.1 |
| Leachable | 17,900 | 0.881* | 315.7 | 4,600 | 0.767* | 69.9 |
NOTES: refer to TABLE 1
*Denotes Cu TSol, generated using a sequential assaying technique to calculate the grade of the soluble copper.
TABLE 4: Cactus Open Pit, inclusive of Cactus West and Cactus East
| PREVIOUS MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of September 28, 2022) |
UPDATED MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2023) |
|||||
| Tons | Grade | Pounds | Tons | Grade | Pounds | |
| kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | kt | Cu% * | Cu Mlbs | |
| Total Measured | N/A | 10,400 | 0.241 | 49.8 | ||
| Leachable | 9,100 | 0.230* | 41.9 | |||
| Total Indicated | 141,900 | 0.505 | 1,431.6 | 209,900 | 0.433 | 1,818.1 |
| Leachable | 66,200 | 0.696* | 919.7 | 138,200 | 0.482* | 1,332.1 |
| Total M&I | 141,900 | 0.505 | 1,431.6 | 220,300 | 0.424 | 1,868.0 |
| Leachable | 66,200 | 0.696* | 919.7 | 147,300 | 0.466* | 1,374.0 |
| Total Inferred | 209,700 | 0.339 | 1,428.7 | 177,900 | 0.328 | 1,168.7 |
| Leachable | 99,700 | 0.334* | 672.1 | 57,500 | 0.315* | 361.8 |
NOTES: refer to TABLE 1
*Denotes Cu TSol, generated using a sequential assaying technique to calculate the grade of the soluble copper.
TABLE 5: Stockpile
| PREVIOUS MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2021) |
UPDATED MINERAL RESOURCE
(As of August 31, 2023) |
|||||
| Tons | Grade | Pounds | Tons | Grade | Pounds | |
| kt | Cu TSol% | Cu Mlbs | kt | Cu Tsol% | Cu Mlbs | |
| Indicated (Oxide) | N/A | 71,100 | 0.153 | 217.3 | ||
| Inferred (Oxide) | 77,400 | 0.144 | 223.5 | 1,200 | 0.127 | 3.0 |
NOTES: refer to TABLE 1
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Labrador Gold (TSXV:LAB), has reported data from its ongoing diamond drilling program at its wholly-owned Kingsway Project, aimed at exploring the Appleton Fault Zone. The company has completed nearly 85,000 metres of the scheduled 100,000-metre drilling initiative. Assays for approximately 6,100 metres of core samples are still pending.
Roger Moss, President and CEO of LabGold commented in a press release: “During the first phase of drilling at DropKick we demonstrated the presence of near-surface gold over significant widths while increasing the strike length of known mineralization which remains open along strike in both directions. Further drilling is required to demonstrate the true potential of this discovery. Planning is currently underway for drilling in The Gap, between Big Vein and Pristine, and to the south of Big Vein towards the recent Knobby discovery. The drilling of targets in these areas is expected to begin before the end of the month. We are excited to start filling in the gaps between the four discoveries made along a 7-kilometre section of the Appleton Fault Zone at Kingsway.”
The first stage of drilling at the DropKick site revealed notable near-surface gold mineralization. Specifically, Hole K-23-248 yielded 1.81 grams per tonne (g/t) of gold over 20.15 metres from a 50-metre depth, which included a 4.5-metre segment grading at 4.14 g/t. Hole K-23-245 also intersected near-surface intervals, with 1.77g/t Au over 5.15 metres from 31.85 metres downhole. Additional drilling data extended the known mineralized area at DropKick to over 360 metres in strike length, which remains open in both directions. Twelve out of 15 drilled holes at DropKick showed gold mineralization, with four containing visible gold.
In the Pristine area, follow-up drilling resulted in an intersection grading at 1.05g/t Au over 11 metres from 90 metres in Hole K-23-276 and 1.28g/t Au over 6.18 metres from 66.47 metres in Hole K-23-272. Mineralization at Pristine mostly occurs above an 86-metre vertical depth and extends over a strike length of about 160 metres.
At the Big Vein site, ongoing drilling intersected 2.76g/t Au over 8.97 metres from 233.56 metres, including a segment that graded at 7.04g/t over 3.09 metres in Hole K-23-278.
The company reported having roughly $10 million in cash, which is expected to cover the remaining 15,000 metres of the planned drilling program and additional exploration.

Highlights from the results are as follows:
| Hole ID | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Au (g/t) | Zone |
| K-23-278 | 233.56 | 242.53 | 8.97 | 2.76 | Big Vein |
| including | 236.00 | 239.09 | 3.09 | 7.04 | |
| K-23-276 | 90.00 | 101.00 | 11.00 | 1.05 | Pristine |
| including | 92.95 | 97.80 | 4.85 | 1.82 | |
| K-23-272 | 66.47 | 72.65 | 6.18 | 1.28 | Pristine |
| including | 68.00 | 70.80 | 2.80 | 2.33 | |
| K-23-260 | 156.57 | 160.00 | 3.43 | 1.06 | Pristine |
| K-23-259 | 67.50 | 68.35 | 0.85 | 1.22 | Pristine |
| K-23-254 | 108.90 | 113.00 | 4.10 | 2.45 | DropKick |
| including | 108.90 | 110.80 | 1.90 | 4.56 | |
| including | 109.40 | 109.70 | 0.30 | 16.68 | |
| K-23-253 | nsv | Big Vein | |||
| K-23-252 | 53.00 | 91.00 | 38.00 | 0.55 | Big Vein |
| including | 60.00 | 64.00 | 4.00 | 1.28 | |
| and | 73.00 | 74.00 | 1.00 | 1.11 | |
| K-23-249 | nsv | Big Vein | |||
| K-23-248 | 50.00 | 70.15 | 20.15 | 1.81 | DropKick |
| including | 55.00 | 70.15 | 15.15 | 2.32 | |
| including | 58.00 | 70.15 | 12.15 | 2.72 | |
| including | 59.90 | 64.40 | 4.50 | 4.14 | |
| K-23-247 | 126.70 | 128.00 | 1.30 | 1.32 | Big Vein |
| 198.00 | 198.95 | 0.95 | 1.20 | ||
| K-23-245 | 10.00 | 12.65 | 2.65 | 1.16 | Dropkick |
| 31.85 | 37.00 | 5.15 | 1.77 | ||
| including | 35.00 | 36.35 | 1.35 | 3.17 | |
| 44.80 | 45.60 | 0.80 | 1.34 | ||
| 53.00 | 54.50 | 1.50 | 1.04 | ||
| 89.00 | 103.00 | 14.00 | 0.60 | ||
| including | 91.95 | 94.00 | 2.05 | 1.42 | |
| 192.00 | 193.15 | 1.15 | 1.90 | ||
| 250.25 | 251.15 | 0.90 | 1.32 | ||
| K-23-244 | 29.00 | 33.00 | 4.00 | 1.10 | Big Vein |
| K-23-243 | nsv | DropKick | |||
| K-23-242 | 224.43 | 225.16 | 0.73 | 1.88 | Big Vein |
| K-23-241 | nsv | Big Vein |
Table 1. Summary of assay results. All intersections are downhole length as there is insufficient Information to calculate true width.
| Hole ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Azimuth | Inclination | Total Depth |
| K-23-278 | 661736 | 5435392 | 37 | 130 | 65 | 420 |
| K-23-276 | 661927 | 5436072 | 56 | 275 | 65 | 200 |
| K-23-272 | 661933 | 5436069 | 59 | 315 | 65 | 278 |
| K-23-260 | 661750 | 5435872 | 58 | 0 | 90 | 209 |
| K-23-259 | 661845 | 5436001 | 53 | 300 | 45 | 191 |
| K-23-254 | 663159 | 5438126 | 55 | 140 | 45 | 160.55 |
| K-23-253 | 661554 | 5435459 | 45 | 20 | 45 | 160 |
| K-23-252 | 661450 | 5435312 | 54 | 125 | 70 | 349 |
| K-23-249 | 661272 | 5435093 | 62 | 145 | 65 | 379 |
| K-23-248 | 663408 | 5438381 | 52 | 140 | 65 | 173 |
| K-23-247 | 661553 | 5435458 | 50 | 125 | 50 | 233 |
| K-23-245 | 663409 | 5438380 | 53 | 140 | 45 | 259 |
| K-23-243 | 663353 | 5438273 | 58 | 140 | 65 | 131 |
| K-23-244 | 661589 | 5435430 | 49 | 140 | 45 | 228 |
| K-23-242 | 661321 | 5435111 | 52 | 145 | 55 | 307 |
| K-23-241 | 661450 | 5435312 | 53 | 125 | 50 | 250 |
Table 2. Drill hole collar details
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

United Lithium (CSE:ULTH) has expanded its holdings at the Kietyönmäki Project in Finland, acquiring an additional 20,000 hectares of land. The new claim reservation is situated around 6 kilometres southeast of the original Kietyönmäki site and encompasses an area known for its lithium-caesium-tantalum pegmatite with historical sampling results of 2% Li2O. This newly acquired territory is viewed as having high potential for further lithium-caesium-tantalum pegmatite discoveries. Earlier strong drill results in the initial 900-hectare plot encouraged the company to increase its land holdings in the region.
Scott Eldridge, United’s President and CEO commented in a press release: “We are pleased to substantially increase our exploration ground in Finland by adding an additional 20,000 hectares creating a district scale project. Historical reports document lithium showings within the new claim boundaries. Finland has demonstrated that it hosts lithium deposits that can be developed. We are encouraged by the success of Keliber and the backing they have received from Sibanye-Stillwater with a total investment of 440 million Euros to obtain 80% ownership in their project. This valuation shows the importance of European lithium projects, and our shareholders are well positioned in the Nordics, with district-scale opportunities in both Finland and Sweden.”
In terms of the drill program, the company plans to release the results from its 2022-2023 program soon. This program included 13 diamond drill holes totalling 1,449.60 meters and 100 shallow exploration percussion drill holes totalling 296.40 meters. The diamond drilling focused on both infill and expansion within the main Kietyönmäki area, while the percussion drilling aimed to discover resources outside that core area.
The expansion brings the project’s total land package to approximately 21,070 hectares, a substantial increase from the original 900 hectares. The newly acquired claim covers around 20,170 hectares, or roughly 200 square kilometres, and is situated 6.1 kilometres southeast of the main exploration permit area of Kietyönmäki. The region was chosen for its known lithium and tungsten-bearing pegmatite dykes, and geological structures that extend from the main Kietyönmäki area. Notably, the area is relatively underexplored but easily accessible and contains known S-type granites. Initial field prospecting and sampling on these new grounds are in the plans, with the objective of identifying drill targets.
United Lithium initially acquired the Kietyönmäki Project in early 2022 through a transaction that saw the company purchase 83.6% of Litiumlöydös Oy, the private entity holding a 100% interest in the project licenses. Following that acquisition, United Lithium expanded the project by 535 hectares in September 2022.
The geological setting of Kietyönmäki includes primarily amphibolites and mica gneisses, among other rock types, and is part of the Häme belt. The area was first discovered in the mid-1980s by the Finnish Geological Survey, which identified a pegmatite swarm at the site. Previous drilling activities have yielded lithium oxide (Li2O) concentrations of up to 1.66% in some drill holes.
The project’s history of exploration began with the Finnish Geological Survey in the 1980s, focusing on what is known as the Main Dyke, the largest lithium-bearing pegmatite body in the area. More recent work was done by the previous operator Avalon in 2016, which involved drilling that further confirmed the resource potential of the Main Dyke.
United Lithium’s forthcoming release of the 2022-2023 drill program results is keenly awaited, as it could provide further insights into the resource potential of both the original and newly acquired land.
Highlights from the property are as follows:
- New claim reservation made over the area with a known LCT-pegmatite that is highly prospective for further discoveries, increasing the total size of the project to more than 21,000 ha;
- 13 diamond drill holes completed with assay results pending, anticipated to be released shortly;
- Previous operators’ historical diamond drilling results include:
- 1.53% Li2O over 23 m drilled by the Finnish Geological Survey (“GTK”)
- 1.10% Li2O over 42 m by previous operator Avalon Minerals Ltd. (“Avalon”);
- Commencement of district scale expanded exploration activity; and
- Finland has proven to be a top jurisdiction to explore for and develop hard-rock lithium projects, with noted success of the Keliber Lithium Project now in the construction phase.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Emerita Resources (TSXV:EMO) has released new drilling results from its ongoing program at La Romanera Deposit, a part of its fully owned Iberian Belt West (IBW) project. The IBW project contains three previously identified massive sulphide deposits: La Infanta, La Romanera, and El Cura. The current results come from the La Romanera deposit and are aimed at tracing the extension of the deposit at greater depths.
The data pertains to drill holes LR154 and LR155, which intercepted polymetallic mineralization roughly 600 meters below the surface, at an elevation of approximately -450m. Both holes reveal mineralization similar in composition, featuring a high pyrite content at the hanging wall side of the lens, which changes to a more chalcopyrite-sphalerite dominant zone closer to the footwall. These intercepts are situated toward the western edge of the deposit and are about 100 meters apart. Their elevation was found to be shallower than initially expected due to a less steep dip angle in this particular area of the deposit. The true thickness of the intercepted zone is nearly 80% of the reported intercept thickness.
Three additional drill holes—LR156, LR157, and LR158—also encountered significant intervals of massive sulphides. Assays for these holes are pending and will be described in greater detail once available. LR156 showed 37.6 meters of massive sulphide, LR157 had 51.6 meters, and LR158, the western-most at this depth, had 5.5 meters.
For drill hole LR154, the grading was 6.3 meters at 0.8% Copper, 3.9% Zinc, 1.6% Lead, 2.82 g/t Gold, and 52.0 g/t Silver within a 27.6-meter grading of 0.5% Copper, 1.5% Zinc, 0.6% Lead, 1.5 g/t Gold, and 25.5 g/t Silver. Drill hole LR155 exhibited 17.2 meters grading 0.2% Copper, 1.3% Zinc, 0.5% Lead, 0.3 g/t Gold, and 19.5 g/t Silver, including 4.0 meters at higher concentrations of these metals.
The exploration team also conducted a down-hole TEM in LR155, indicating a strong geophysical anomaly continues at depth. This will be further tested by drilling. Currently, Emerita Resources is operating four rigs at La Romanera with the aim of verifying the continuity of mineralization below the current NI 43-101 mineral resource estimate. The company also aims to increase the drill density in this area for inclusion in an updated mineral resource estimate, and post-metallurgical program.
Drilling productivity is currently constrained by fire ban restrictions, which prohibit the use of heavy equipment from approximately noon to 8:00 PM. These restrictions, extended due to a particularly hot and dry summer, are expected to last until mid-October. Once lifted, the company plans to begin drilling at the Nuevo Tintillo Project, for which permits and access agreements are already in place.
Metallurgical samples for the project are being processed in a United Kingdom lab. While the grinding test work is complete, mineral separation work is now beginning. The metallurgical program is running 2-3 weeks behind schedule, with initial results now anticipated in November.
Table 1: Diamond drill hole data
| DDH | Easting | Northing | Elevation | azimuth | dip | depth (m) |
FROM | TO | Width (m) |
Cu_% | Pb_% | Zn_% | Au_g/t | Ag_g/t | LENS |
| LR154 | 646716 | 4172736 | 146 | 235 | -68 | 680.9 | 640.0 | 667.5 | 27.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.49 | 25.5 | LL |
| incl. | 653.9 | 660.2 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 3.9 | 2.82 | 52.0 | LL | ||||||
| LR155 | 646751 | 4172871 | 154 | 231 | -56 | 782.7 | 725.9 | 743.1 | 17.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.34 | 19.5 | LL |
| incl. | 739.1 | 743.1 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 4.7 | 0.60 | 57.0 | LL |
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Fortuna Silver Mines (TSX:FVI) has completed its acquisition of Chesser Resources Limited, according to official statements. Under the terms of the deal, Fortuna acquired all of Chesser’s fully paid ordinary shares, exchanging 0.0248 of one Fortuna common share for each share of Chesser. At the close of the transaction, Fortuna issued 15,545,368 shares in return for Chesser’s shares. These newly issued shares account for approximately 5.1% of Fortuna’s total issued and outstanding shares on an undiluted basis.
Jorge A. Ganoza, President and CEO of Fortuna, commented in a press release: “With the acquisition of Chesser, Fortuna continues to strengthen its presence in West Africa. Senegal is a mining friendly and highly prospective jurisdiction, and we are excited about the growth potential that Chesser’s Diamba Sud Gold Project provides. We look forward to integrating Diamba Sud into our global portfolio, focusing on exploration to unlock value, and partnering with the local communities and stakeholders as we continue to advance the project.”
The acquisition was conducted via a statutory scheme of arrangement, compliant with Part 5.1 of the Australian Corporations Act 2001. As a result of the transaction, Chesser Resources is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of Fortuna Silver Mines, and its shares are expected to be delisted from the ASX within one to two business days. The purchase expands Fortuna’s operations into West Africa, adding the Diamba Sud Gold Project in Senegal to its portfolio. Chesser had held approximately 872 square kilometers of prospecting ground in Senegal, which is close in proximity and similar in geological features to other significant gold mines in the region. The Diamba Sud project itself contains four open-pittable high-grade gold deposits, as well as several untested anomalies. Fortuna plans to focus initially on exploration to expand the mineral resources at Diamba Sud, before moving the project to the development stage.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

K2 Gold (TSXV:KTO), has reported the completion of its 2023 Reverse Circulation (RC) drilling program at the Wels Project. Situated in west-central Yukon, the Wels Project is 60km south of Newmont’s Coffee gold deposit and 23km east of a road-accessible staging area. The team overseeing the Wels Project is composed of experts who have previously contributed to significant projects in the Yukon, including the development of Kaminak’s Coffee Gold deposit, now owned by Newmont, and Underworld Resources’ White Gold deposit, currently under the ownership of White Gold Corporation.
The drilling campaign achieved a total of 1,961 meters across 12 drill holes. The Wels Project is distinguished by its high-grade, structurally controlled gold system, showing similarities to other high-profile projects in Yukon’s White Gold district, including Newmont’s Coffee Project and White Gold Corporation’s Golden Saddle deposit.
Anthony Margarit, President and CEO of K2 Gold commented in a press release: “The 2023 RC drill program was designed to test 5 target areas across the property. A combination of efficient drilling, and logistics led to a 25% increase in metres drilled and allowed K2 to drill 2 holes more than planned. A total of 12 holes were drilled, with mineralization observed in all holes, several of which test kilometre-scale structures. We look forward to releasing assay results to the public in the near future.
John Robins, Executive Chairman K2 Gold also commented: “Wels bears striking similarities to the Coffee Gold deposit we discovered in 2010. Similar to what we saw in the early days of exploration at the Coffee project extensive kilometre-scale gold-in-soil anomalies with associated arsenic and antimony + strong geophysical anomalies are localized around fault corridors which control mineralization, the same characteristics are observed at the Wels property.”
The geology of the Wels Project features a high-angle, WNW-trending fault system, and all types of rocks at the site have demonstrated mineralization in drilling, trenching, or surficial sampling. Previous drilling initiatives focused mainly on the granite-hosted Saddle target, where they found high-grade gold intersections. The 2023 drilling was specifically planned to test various soil and trench gold anomalies, along with electromagnetic Very Low Frequency (VLF) geophysical anomalies throughout the property.
Starting at the Saddle target, the drilling efforts aimed to cover the entire section, ranging from North Saddle to South Saddle. Neither of these areas had been drilled before. A total of 1,042.42 meters was drilled across this section. The drilling operations then moved to Chai and Pekoe targets, both of which had not been drilled previously and indicated high-grade gold in soil, rock, and trench samples. At Chai, three holes covering 432.82 meters were completed, and at Pekoe, two holes comprising 338.33 meters were drilled. The final 147.83-meter hole was drilled at West Saddle, more than 100 meters away from the main Saddle target where K2 had previously drilled.
All the drilled holes revealed structurally controlled pyrite-arsenopyrite mineralization and quartz veining across various types of rock, including granite, diorite, gabbro, quartzite, and siltstone.
K2 Gold maintains a 90% vested interest in the Wels Project. The remaining 10% is owned by Go Metals Corporation as part of a joint venture agreement. Under the agreement, K2 Gold is responsible for funding the project through the completion of a preliminary economic assessment. Subsequent project expenditures will be funded on a 90/10 proportionate basis between K2 Gold and Go Metals, with K2 Gold serving as the project manager. The property is also subject to a 3% Net Smelter Return (NSR), of which 2% can be acquired by K2 under specified terms.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Faraday Copper (TSX:FDY) recently announced the results of gold assays from archived material from the Childs Aldwinkle breccia at their Copper Creek project in Arizona, USA. The samples, which had not been previously tested for gold, were analyzed to improve data coverage. The outcomes have reinforced the company’s position that the project holds extractable gold, adding another layer of value to the site.
Paul Harbidge, President and CEO, commented in a press release: “We are pleased to provide the first results of the gold program after completing analysis of the Childs Aldwinkle breccia. The results show near-surface gold mineralization in the current resource pit shell and demonstrate the potential to add a gold by-product, further enhancing the value of the project. The team has been able to advance our thesis of payable gold in the resource by utilizing the historical drill core and pulps that previous operators did not analyze for gold. With Childs Aldwinkle assay results now received, the Company is currently preparing samples from other high-priority breccias and we look forward to presenting results as they are available.”
In past results, the focus of sample analysis was largely on copper, with gold getting considerably less attention. Faraday Copper aims to increase the amount of gold data available for potential incorporation into future resource updates. Besides gold, the samples are also being reassessed for copper, silver, and molybdenum to cross-check historical findings. Childs Aldwinkle is the first breccia selected for this multi-elemental analysis.

The results from Childs Aldwinkle indicated a robust correlation between gold and copper, observed as a 1:10 gold (g/t):copper (%) ratio. According to a technical report effective as of May 3, 2023, the breccia is estimated to contain about 3.3 million tonnes of mineralized material. This correlation suggests that the gold is mineralogically bound with copper and is expected to be included in copper concentrate. However, it’s important to note that this ratio and gold presence have not yet undergone a complete metallurgical or economic assessment, which means it is not yet classified as part of an official mineral resource.
Faraday Copper has initiated a metallurgical program to gather more information on the recoverability of gold. This will involve variability tests across multiple breccia domains to further understand how gold behaves in different settings.
Looking ahead, Faraday Copper plans to continue re-analyzing older samples, with an eye towards potentially including more gold data in future resource estimations. Additional areas under consideration for this gold program include the Copper Prince and Pole breccias, as well as the Keel underground zone. A new drilling program is set to kick off in October 2023, aiming to expand the Mineral Resource Estimate, better outline high-grade mineralized zones, and perform reconnaissance drilling on new targets.
The company is working towards releasing an updated technical report in the first half of 2025. This will include findings from their upcoming Phase II and III drilling programs, the ongoing gold program, and metallurgical studies.
Highlights from the results are as follows:
- Significantly increased analytical coverage for gold at Childs Aldwinkle with 743 new gold assay results in addition to 120 historical gold results.
- Examples of intercepts with new gold assays and re-assayed copper include:
- 219.46 m (“metres”) at 3.29% copper and 0.31 g/t gold from 24.38 m in drill hole CA-5R;
- 94.49 m at 1.12% copper and 0.13 g/t gold from 341.38 m in drill hole CA30+3; and
- 56.38 m at 1.32% copper and 0.29 g/t gold from 150.88 m in drill hole CC-2.
- A weighted average of 0.16 g/t gold and 1.52% copper is calculated for mineralized intercepts for which gold analytical data is available1.
- Gold and copper are well-correlated on an intercept basis with an overall ratio of approximately 1:10 gold (g/t):copper (%) at Childs Aldwinkle.
- Historical metallurgical test work suggests high gold recoveries in the copper concentrate. The Company has initiated a metallurgical program to confirm gold recoveries.
- As part of the gold program, copper was re-assayed. These results confirm historical data, providing additional confidence in the database.
- Phase III drill program is expected to commence in October 2023.
Table 1: Intercept values at the Childs Aldwinkle breccia
| Drill Hole ID | From | To | Length | True width | Cu | Au | Ag | Mo |
| (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (%) | (g/t) | (g/t) | (%) | |
| CA-4R | 12.19 | 30.84 | 18.65 | N/A | 0.48 | 0.02 | 1.47 | 0.0042 |
| CA-4R | 64.01 | 82.30 | 18.29 | N/A | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.0016 |
| CA-5R | 24.38 | 243.84 | 219.46 | N/A | 3.29 | 0.31 | 13.88 | 0.0770 |
| CA28+3A | 441.96 | 496.83 | 54.87 | 32 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 1.30 | 0.0004 |
| CA28+4 | 512.07 | 566.93 | 54.86 | 30 | 1.84 | 0.17 | 4.69 | 0.0320 |
| CA30+3 | 341.38 | 435.87 | 94.49 | 60 | 1.12 | 0.13 | 4.55 | 0.0230 |
| CA30+4 | 438.91 | 496.83 | 57.92 | 36 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 1.08 | 0.0006 |
| CA32+3 | 341.38 | 390.15 | 48.77 | 34 | 1.64 | 0.21 | 5.50 | 0.0320 |
| CA32+5 | 330.40 | 360.88 | 30.48 | 21 | 0.99 | 0.10 | 3.69 | 0.0800 |
| CA32+6 | 256.03 | 289.56 | 33.53 | 22 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 0.0031 |
| CA34+3 | 234.70 | 271.27 | 36.57 | 22 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 2.26 | 0.1106 |
| CA34+4 | 234.70 | 280.42 | 45.72 | 28 | 1.57 | 0.10 | 5.62 | 0.0285 |
| CA34+4A | 243.84 | 274.32 | 30.48 | 19 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 3.17 | 0.1007 |
| CA35.5+1 | 176.78 | 234.70 | 57.92 | 44 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 1.85 | 0.0130 |
| CA35.5+3 | 225.55 | 234.70 | 9.15 | 7 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.0016 |
| CA36+7 | 249.94 | 277.37 | 27.43 | 22 | 2.49 | 0.24 | 9.74 | 0.0867 |
| CA37.5+1 | 146.30 | 179.83 | 33.53 | 28 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 1.15 | 0.0113 |
| CA37.5+1A | 124.97 | 173.74 | 48.77 | 44 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 2.25 | 0.0746 |
| CA37.5+2 | 134.11 | 158.50 | 24.39 | 22 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.0601 |
| CA38+7 | 149.35 | 184.10 | 34.75 | 22 | 2.36 | 0.19 | 9.31 | 0.0179 |
| CA40+7 | 116.43 | 135.64 | 19.21 | 17 | 3.48 | 0.24 | 10.59 | 0.0649 |
| CC-2 | 150.88 | 207.26 | 56.38 | 36 | 1.32 | 0.29 | 5.53 | 0.0205 |
| MET-2CA | 45.72 | 169.16 | 123.44 | N/A | 3.79 | 0.33 | 11.57 | 0.0486 |
| MET-3CA | 45.72 | 152.40 | 106.68 | N/A | 3.71 | 0.35 | 11.27 | 0.0169 |
| FCD-23-023 | 184.72 | 230.61 | 45.89 | 35 | 1.68 | 0.33 | 5.55 | 0.0280 |
| FCD-23-027 | 390.72 | 408.98 | 18.26 | 9 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 0.0080 |
| CA-9R | 164.59 | 182.88 | 18.29 | N/A | 2.76 | 0.28 | 8.20 | 0.0206 |
| CATECH | 237.74 | 243.23 | 5.49 | N/A | 1.61 | 0.23 | 9.43 | 0.0014 |
| CA28+8 | No significant intercepts and incomplete gold data | |||||||
| CA30+6 | No significant intercepts | |||||||
| CA35.5+2 | No significant intercepts | |||||||
| CA36.5+2 | No significant intercepts | |||||||
| CA36.5+3 | No significant intercepts | |||||||
| CA36+8 | No significant intercepts | |||||||
Notes: Copper, silver and molybdenum columns indicate re-assayed metal values. Drill holes MET-2CA and MET-3CA were not re-assayed as part of this program. Drill holes CA40+7 and CC-2 are composite samples. For drill holes CA-9R and CATECH, gold data does not cover the entire mineralized intercept and lengths listed are for the portion for which gold data is available. True widths are approximate.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

The City of Casa Grande has given the green light for the rezoning of the northern section of the MainSpring Property, known as “Parks/Salyer South,” to Industrial use for Arizona Sonoran Copper (TSX:ASCU). This approval paves the way for Arizona Sonoran Copper to kick off drilling activities. The company is currently in the process of developing an exploration plan. Meanwhile, the southern parcel of Parks/Salyer South is still undergoing rezoning and a General Plan Amendment with the City of Casa Grande.
Travis Snider, VP Sustainability and External Relations commented in a press release: “Our team is appreciative of the ongoing support from the city of Casa Grande and our Stakeholders in every step of redeveloping the Cactus Mine. Rezoning the north parcel continues to open up new land at Cactus for future operations, and adds the potential for incremental mineral resource growth.”
In addition to the rezoning, Arizona Sonoran Copper has secured a 2.5-acre Mineral Exploration Permit (MEP) within the Parks/Salyer deposit from Arizona State Lands. This acquisition will offer the company more operational flexibility and positions it for low-risk, high-impact exploration targets. The MEP is situated at the southern edge of the Parks/Salyer deposit and intersects with Parks/Salyer, Bronco-Creek, and Parks/Salyer South properties. The permit will also enhance accessibility to mineralized material and mitigate any potential setbacks in mine planning activities adjacent to this parcel.
For context, the Parks/Salyer mineral resource has an estimated 2.9 billion pounds of copper with a grade of 1.015%, categorized as inferred. The mineral resource is presently confined to the Parks/Salyer border. Arizona Sonoran Copper plans to release an updated mineral resource report for the entire Cactus Project, which includes Parks/Salyer, in the fourth quarter of 2023.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.

Solaris Resources (TSX:SLS) (OTCQB:SLSSF) has announced the appointment of China International Capital Corporation Limited (CICC) as its financial advisor for Chinese operations. CICC is a global investment bank headquartered in Beijing, with more than 200 branches across China and additional offices in Hong Kong and other international locations. The firm holds a strong position in the Chinese M&A market, particularly in transactions related to the mining sector. This move comes after Solaris Resources has received multiple acquisition proposals for its Warintza Project in Ecuador.
Mr. Richard Warke, Executive Chairman, commented in a press release: “Warintza is a very special asset that has the potential to create tremendous long-term value for all stakeholders by unlocking one of the last major greenfield districts at low elevation and adjacent to infrastructure in the global copper industry. The Company has a rich opportunity to significantly grow the Project while advancing it through technical studies and permitting with financing consistent with my commitment to minimize shareholder dilution.”
CICC will be responsible for evaluating the viability of these proposals, among other strategic considerations. The appointment is particularly timely given the current surge of interest from Chinese investors in Ecuador, as reflected in recent news reports. Companies engaged in exploration projects in the country, like Solaris, are increasingly receiving calls and inquiries about potential collaborations or acquisitions.
The above references an opinion and is for information purposes only. It is not intended to be investment advice. Seek a licensed professional for investment advice. The author is not an insider or shareholder of any of the companies mentioned above.
If you would like to receive our free newsletter via email, simply enter your email address below & click subscribe.
CONNECT WITH US
Tweets
Tweet with hash tag #miningfeeds or @miningfeeds and your tweets will be displayed across this site.
MOST ACTIVE MINING STOCKS
Daily Gainers
 Lincoln Minerals Limited Lincoln Minerals Limited |
LML.AX | +125.00% |
      |
GCR.AX | +33.33% |
      |
CASA.V | +30.00% |
      |
AHN.AX | +22.22% |
      |
ADD.AX | +22.22% |
      |
AZM.V | +21.98% |
      |
NSE.V | +21.05% |
      |
DYG.V | +18.42% |
      |
AAZ.V | +18.18% |
      |
GLA.AX | +17.65% |


 Follow us on Twitter
Follow us on Twitter Become our facebook fan
Become our facebook fan